Medical Errors
Article Sections
Introduction
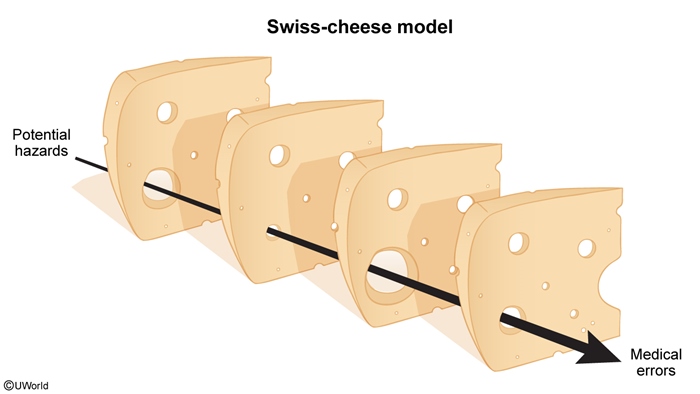
Medical errors are unintended acts—either of omission (ie, not doing something that should have been done, such as not administering a needed medication) or commission (ie, doing something incorrect, such as administering the wrong medication)—that involve failure of a planned action to be completed as intended or use of a wrong plan to achieve an outcome. Such errors are a leading cause of preventable injury and death in health care, occurring in both the inpatient and outpatient settings, and entail significant ethical and financial costs. Modern patient safety science emphasizes a systems-based, nonpunitive approach to understanding and mitigating error, with a focus on improving reliability, transparency, and organizational learning. This article provides a review of medical errors, including error definitions, contributing factors, and recommended strategies to prevent errors.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Medical Errors article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures