Transient Synovitis
Article Sections
Introduction
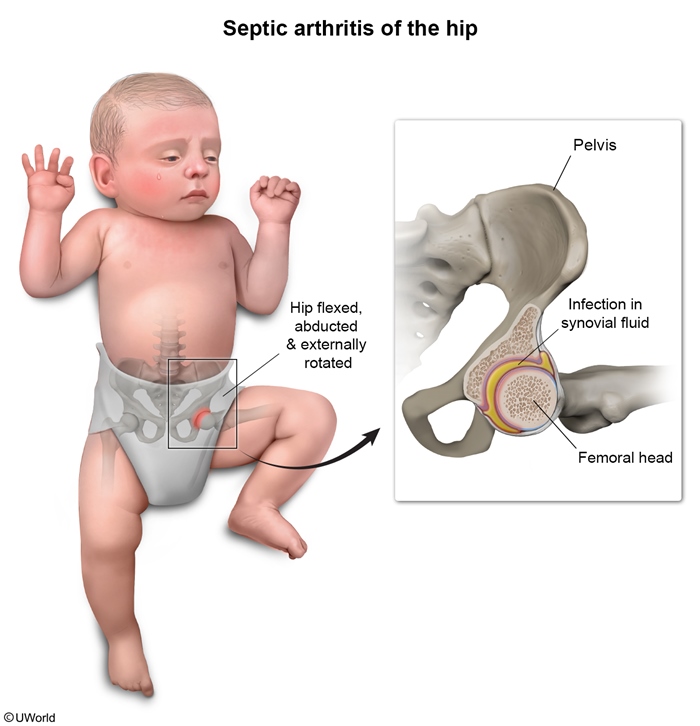
Transient synovitis, a self-limiting inflammatory condition of the joint synovium, classically presents with hip pain in well-appearing young children following a viral illness. This condition is a diagnosis of exclusion and must be distinguished from potentially life-threatening conditions such as septic arthritis.
Pathogenesis
Transient synovitis is the most common cause of acute hip pain in children. This benign condition is characterized by inflammation of the synovium (inner lining of the joint). Effusion develops in the joint space, and the increased pressure results in pain, decreased range of motion, and limp. Although the cause is unknown, it typically occurs in children age 3-8 following a mild viral illness (eg, gastroenteritis, respiratory infection) or, less commonly, after minor trauma involving the hip (eg, sports injury). In some cases, no preceding trigger is identified.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Transient Synovitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures