Elbow Tendinopathy
Article Sections
Introduction
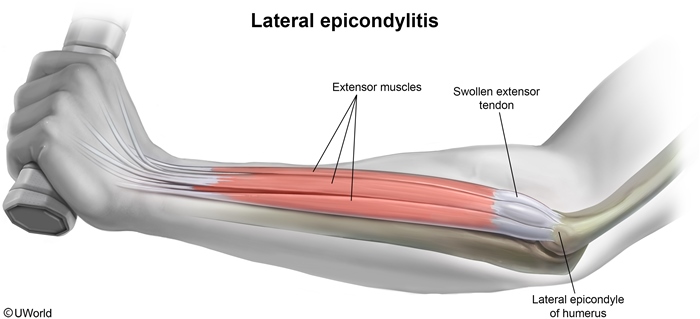
Elbow tendinopathy is a common overuse injury involving the tendons that attach to the humeral epicondyles. The 2 main types are lateral epicondylitis, which involves the wrist extensor tendons, and medial epicondylitis, which involves the flexor-pronator tendons.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
Elbow tendinopathy is primarily a degenerative, instead of an inflammatory, process. Repetitive, forceful use of the wrist extensor or flexor muscles can lead to microtrauma at the tendon origin. This results in angiofibroblastic tendinosis, a degenerative process marked by excess fibroblasts, disorganized collagen, and neovascularization without a significant inflammatory infiltrate. Tendinosis weakens the tendon-bone junction and leads to pain, swelling, and functional impairment (Figure 1). Therefore, common risk factors include a sudden increase in activity level, poor athletic technique or ergonomics, and smoking and obesity (which are linked to poor tendon healing).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Elbow Tendinopathy article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures

Images