Nonaccidental Trauma In Children
Article Sections
Introduction
Nonaccidental trauma (NAT) occurs when a caregiver intentionally injures a child. NAT is the leading cause of traumatic injury in infants age <1. Healthcare professionals must be vigilant in identifying signs of NAT and protecting the child.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
NAT occurs when a caregiver intentionally injures a child. NAT can occur in the setting of:
- Physical abuse (eg, shaking, scalding)
- Neglect (ie, malnutrition resulting in failure to thrive)
- Sexual abuse
Therefore, risk factors include child-related, caregiver-related, and environmental factors (Table 1).
Child-related risk factors
- Age (infants and toddlers at highest risk due to physical vulnerability and dependence on the caregiver)
- Physical, intellectual, or emotional disabilities or chronic illnesses
Caregiver-related risk factors
- Substance use disorders
- Mental health disorders (eg, depression, anxiety, impulse control disorders)
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Nonaccidental Trauma In Children article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
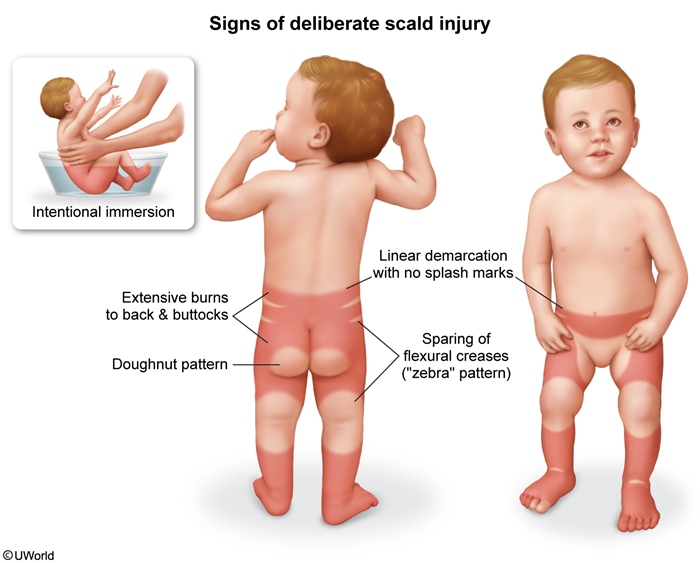
Figure 1
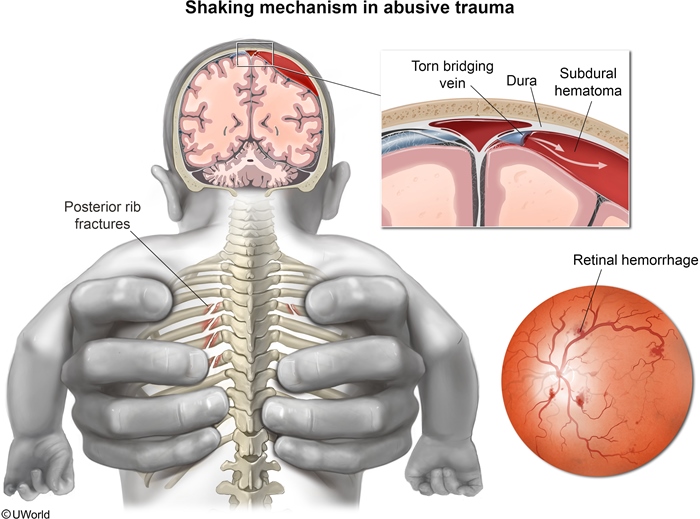
Figure 2
Images
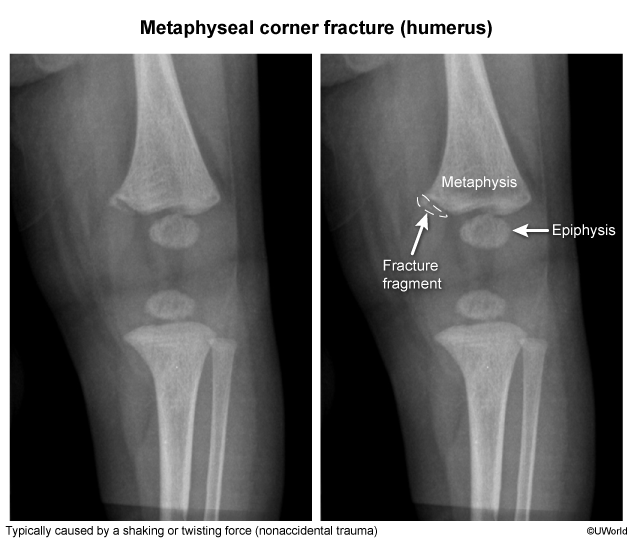
Image 1
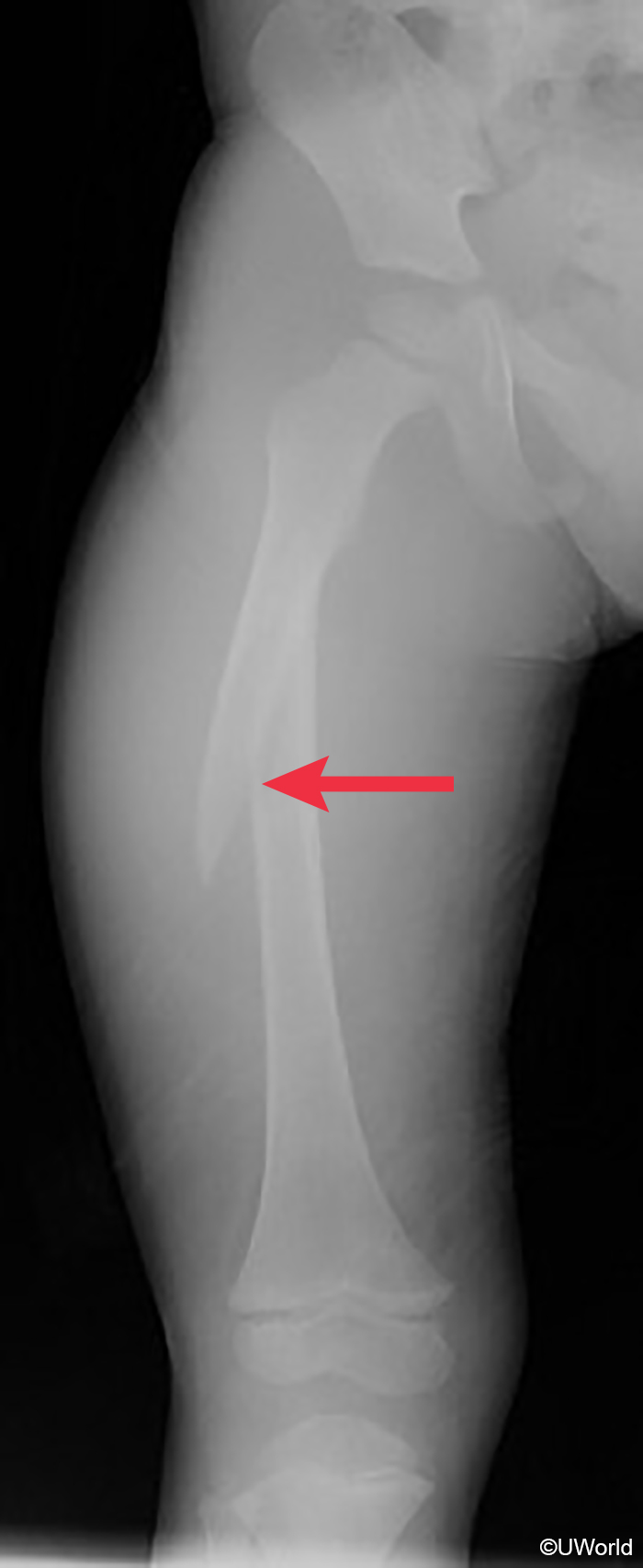
Image 2
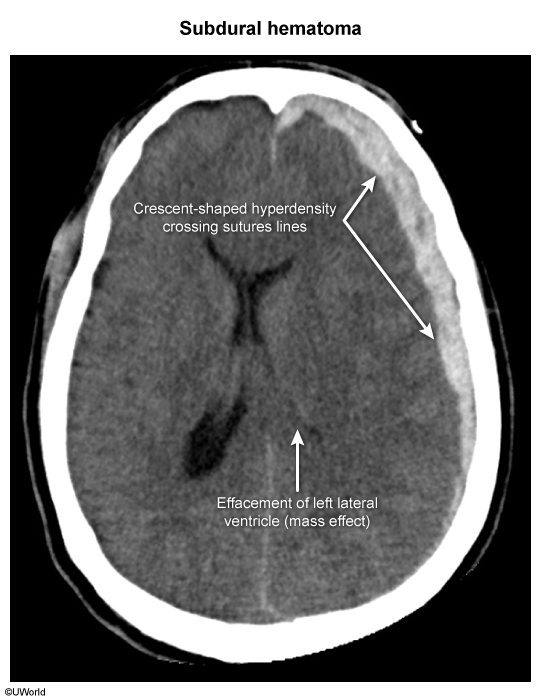
Image 3
Tables
Table 1