Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
Article Sections
Introduction
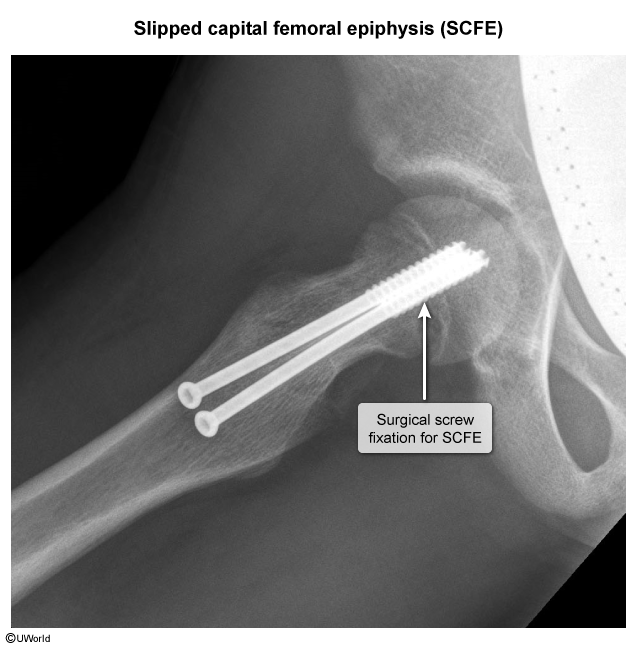
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) is a disorder characterized by displacement of the femoral head from the femoral neck through the growth plate. It predominantly affects adolescents undergoing accelerated linear growth.
Pathophysiology
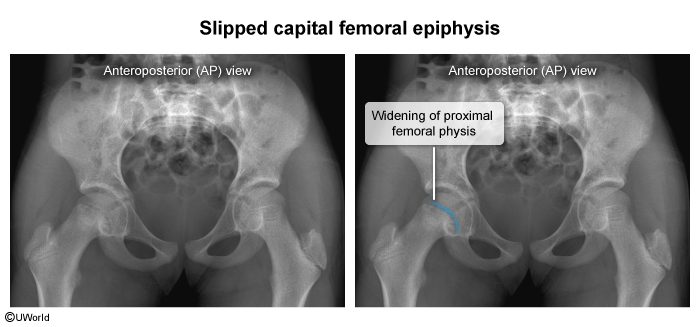
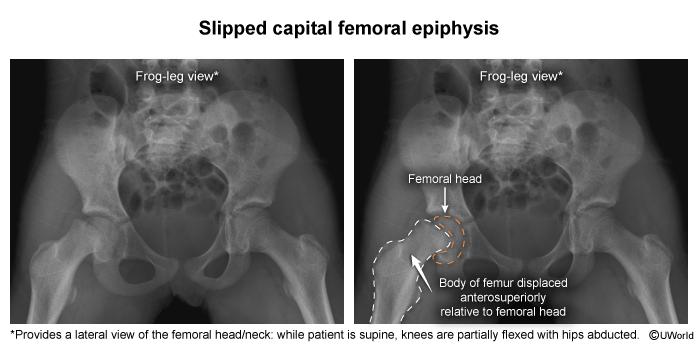
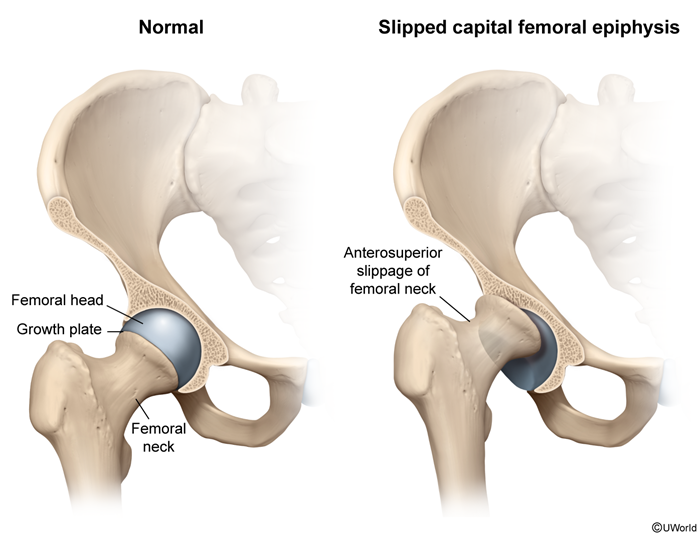
SCFE occurs due to excessive shearing forces at the proximal femoral physis (growth plate). When the shearing forces exceed the strength of the physis, a fracture occurs within this growth plate, resulting in anterosuperior displacement of the proximal femur diaphysis relative to the femoral head (Figure 1). On imaging, this may give the appearance that the femoral head has been displaced posteriorly, but it actually is in normal position within the acetabulum.
Risk factors
SCFE occurs when the shearing forces at the femoral head overcome the strength of the proximal femoral growth plate. Risk factors include:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images