Bursitis
Article Sections
Introduction
Bursitis involves inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion and lubricate areas where tendon, muscle, and bone rub against each other. Any bursa in the body can be affected (eg, olecranon, trochanteric, anserine, prepatellar), resulting in swelling and pain with movement of the joint. Bursitis can be classified as noninfectious or infectious, with each having a different presentation and treatment.
Anatomy
Bursae are located throughout the body (~160 in all) and are classified according to location:
- Superficial bursae (eg, prepatellar, olecranon) are located in the subcutaneous tissue between skin and bone.
- Deep bursae (eg, subacromial, trochanteric, pes anserine) are located between adjacent muscle or between bone and adjacent muscle and/or tendon.
Pathophysiology
Bursitis can arise from noninfectious or infectious etiologies (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Bursitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages
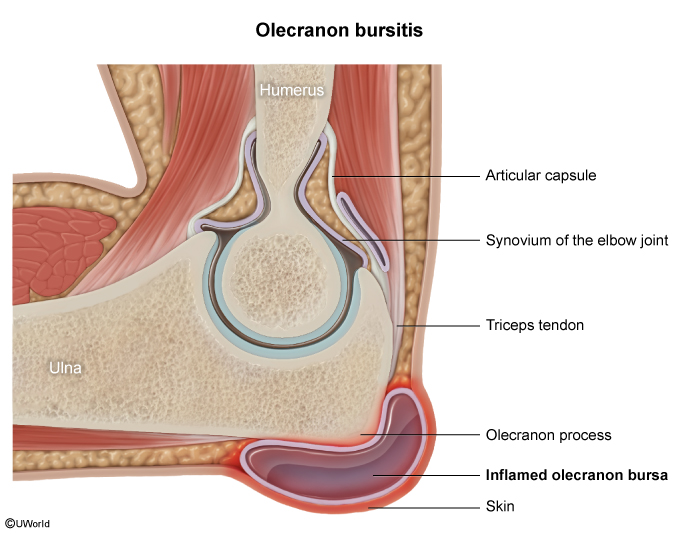
Image 1
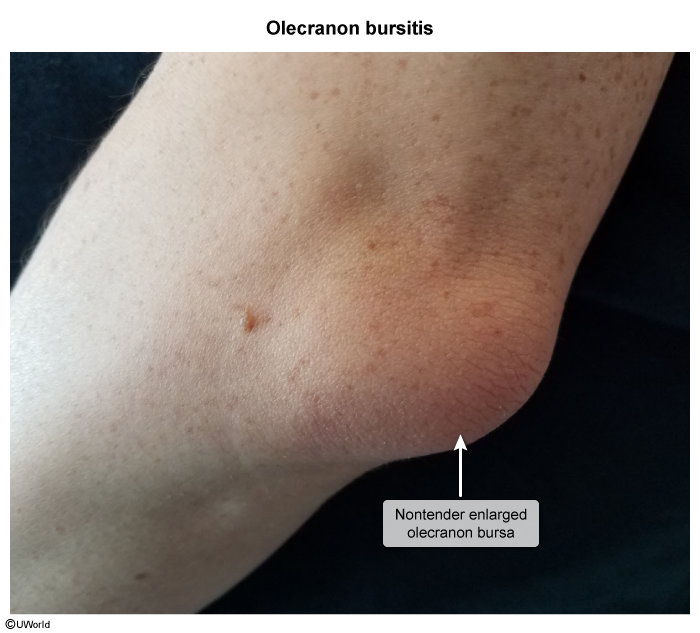
Image 2
Tables
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3
Table 4