Chronic Cough
Article Sections
Introduction
Cough is generally classified as acute, subacute, or chronic based on duration:
- Acute: <3 weeks.
- Subacute: 3-8 weeks.
- Chronic: >8 weeks (adults) or >4 weeks (children).
Acutely, cough is predominantly caused by respiratory tract infection (eg, viral upper respiratory infection, bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia). Subacutely, most cases represent a postinfectious cough. In contrast, chronic cough has a much wider range of causes including airway disease, acid reflux, and other conditions discussed below.
Pathogenesis
Chronic cough arises from prolonged activation of the cough reflex due to a persistent irritant or neural hypersensitivity caused by repeated mucosal trauma from coughing itself (ie, vicious cycle).
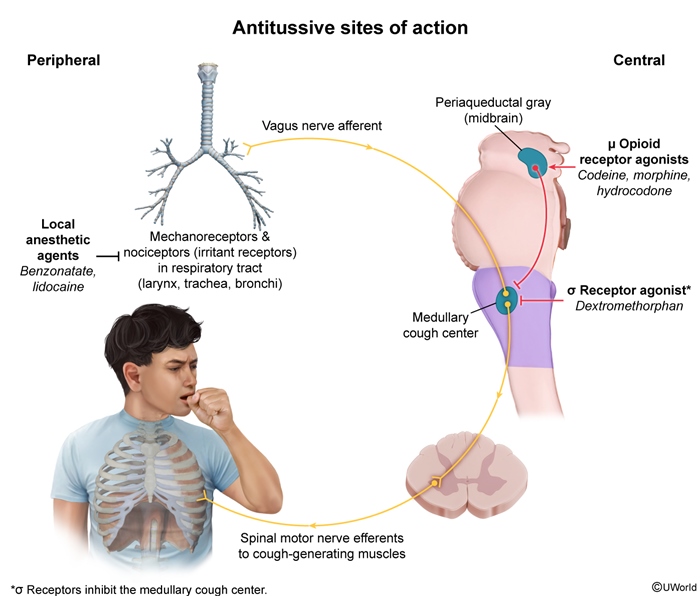
Cough reflexThe cough reflex consists of 3 elements:
- Afferent (sensory) arc: Cough is stimulated by vagus sensory branches that innervate the larynx, airway mucosa, and lung parenchyma. The glossopharyngeal (pharynx) and trigeminal (paranasal sinuses) nerves also contribute but to a lesser extent. There are 2 major sensory fiber types:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Chronic Cough article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures