Silicosis
Article Sections
Introduction
Occupational lung diseases fall into 2 broad categories.
- Occupational asthma: represents bronchospastic airway disease due to a workplace allergen or pollutant.
- Occupational interstitial lung diseases (ILDs): include occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis (granulomatous ILD due to inhaled organic antigens) and pneumoconiosis (fibrotic ILD due to inhaled inorganic dusts). The 3 pneumoconioses (pneumo = lung, konis = dust) are coal workers' pneumoconiosis (aka "black lung") from coal dust, asbestosis from asbestos fibers, and silicosis from silica crystals.
This article addresses silicosis, the most common form of occupational ILD worldwide. Silicosis is caused by the inhalation of crystalline silica dust from activities such as stonecutting and sandblasting. Exposure over several decades leads to lung inflammation and fibrosis. Silicosis is associated with chronic pulmonary infections (eg, tuberculosis, fungi), systemic autoimmune conditions (eg, rheumatoid arthritis), and lung cancer.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Silicosis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages
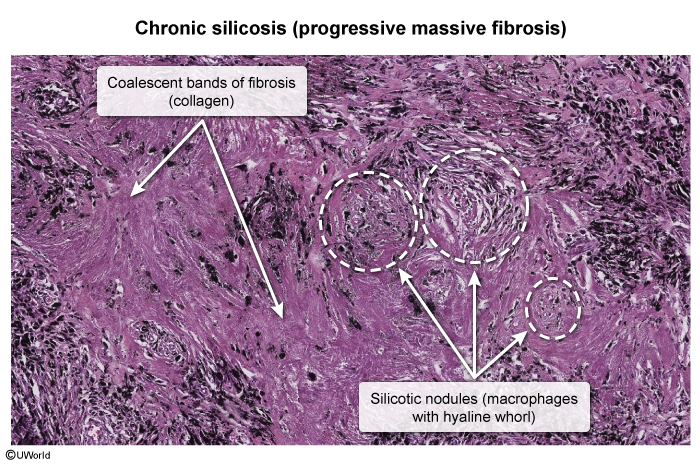
Image 1
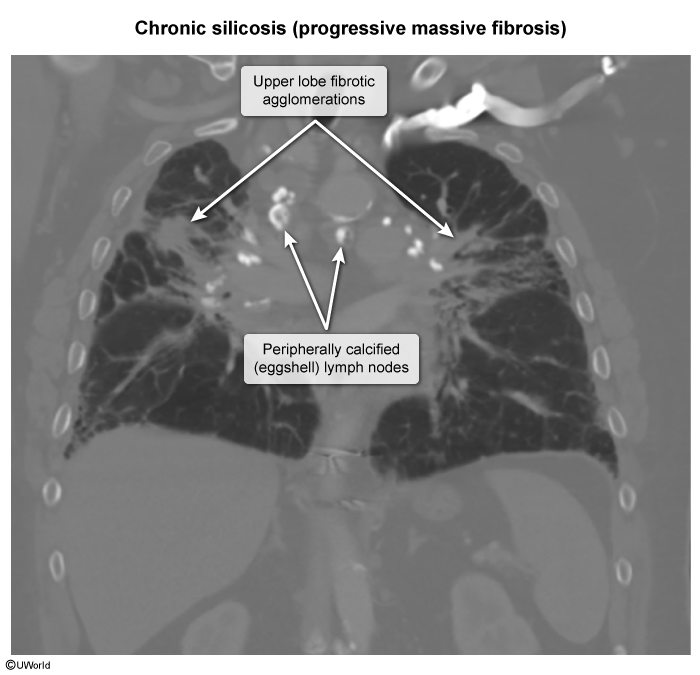
Image 2
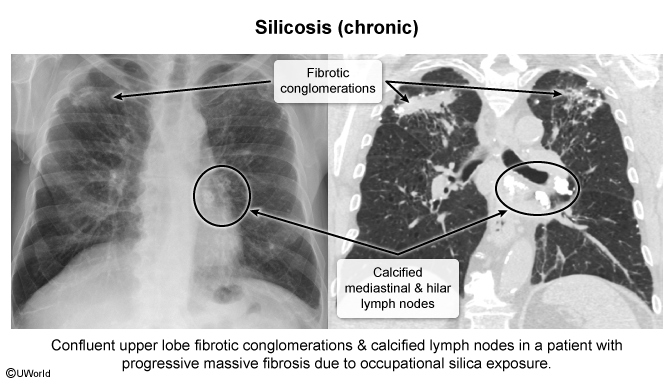
Image 3
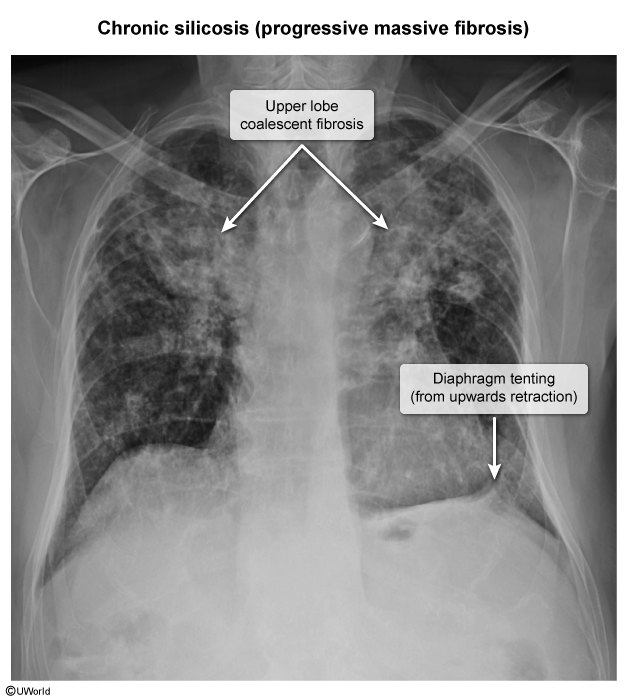
Image 4
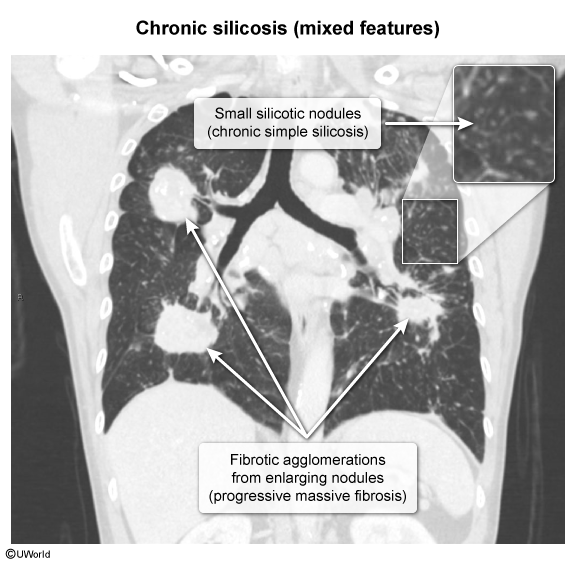
Image 5
Tables
Table 1