Asbestos
Article Sections
Introduction
Occupational lung diseases fall into 2 broad categories.
- Occupational asthma: represents bronchospastic airway disease due to a workplace allergen or pollutant.
- Occupational interstitial lung diseases (ILDs): include occupational hypersensitivity pneumonitis (granulomatous ILD due to inhaled organic antigens) and pneumoconiosis (fibrotic ILD due to inhaled inorganic dusts). The 3 pneumoconioses (pneumo = lung, konis = dust) are coal workers' pneumoconiosis (aka "black lung") from coal dust, asbestosis from asbestos fibers, and silicosis from silica crystals.
This article addresses asbestosis and other asbestos-related conditions. Asbestos is a naturally occurring, crystalline fiber composed of silica. Given its fire-retardant and insulating properties, it was popular for mid-century construction (eg, in walls, attics, ducts, and pipes), but it has been largely phased out of modern construction because of its health effects. However, it remains an important cause of lung disease due to delayed effects of exposure decades ago.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Asbestos article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
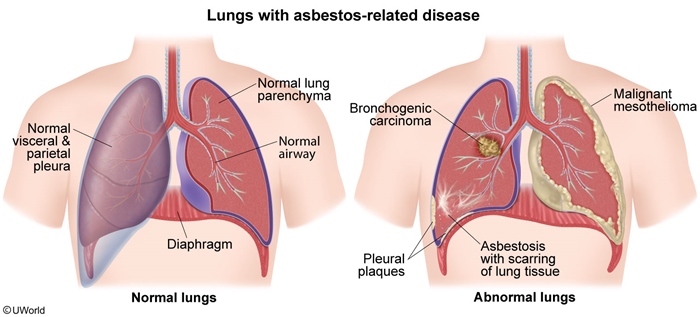
Figure 1
Images
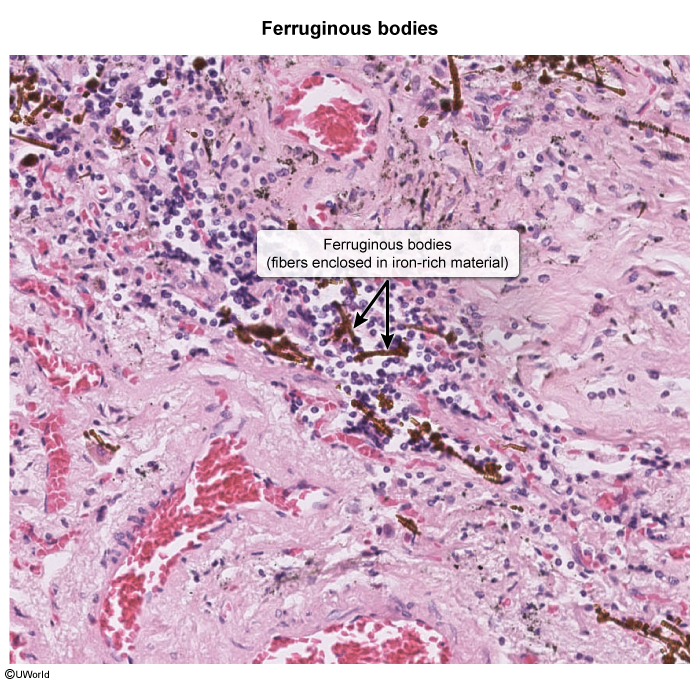
Image 1
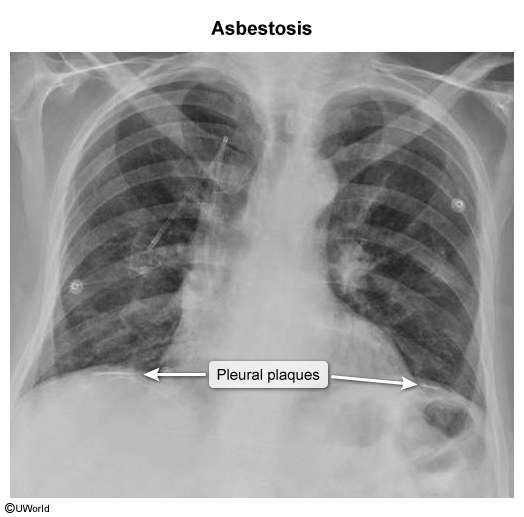
Image 2
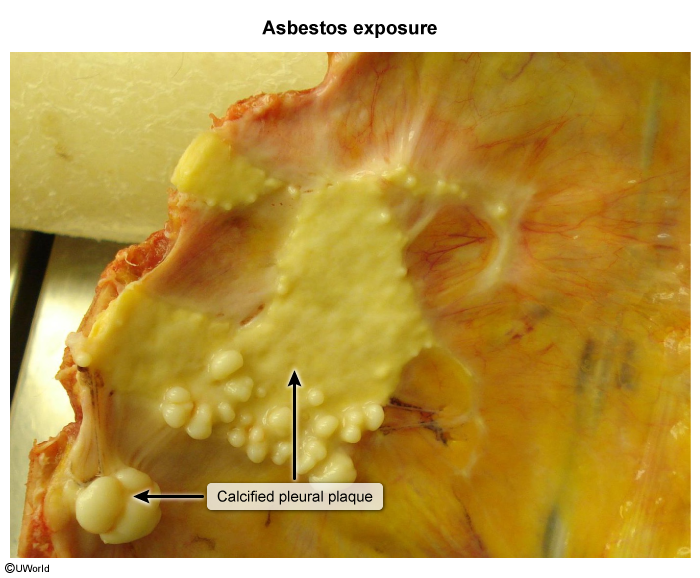
Image 3
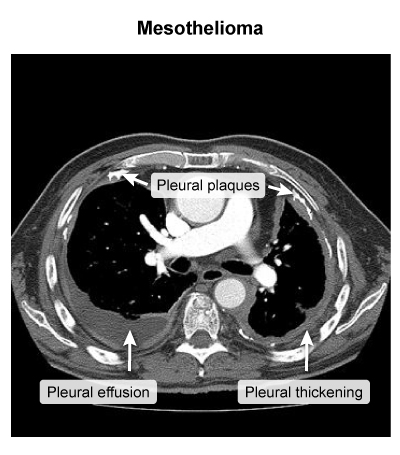
Image 4
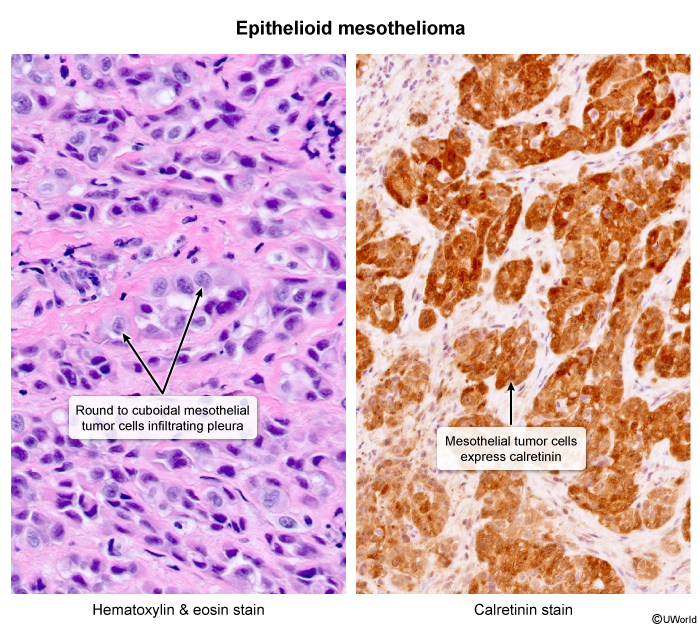
Image 5