Interstitial Lung Disease
Article Sections
Introduction
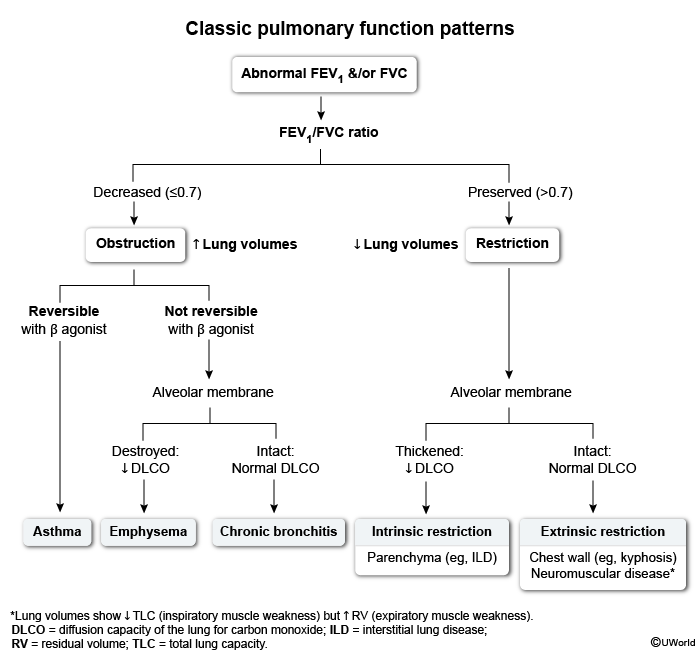
The lung interstitium comprises the extracellular connective tissue between alveolar epithelium and the capillary endothelium. Interstitial lung disease (ILD) encompasses >150 distinct conditions that cause inflammation, fibrosis, or proliferation of this space, resulting in impaired gas exchange and respiratory mechanics. This article provides a conceptual framework for understanding ILD, with specific details of some important ILDs included for completion.
Pathogenesis and classification
ILD classification can be frustrating due to the diverse terminology used to describe equivalent or related conditions across clinical, radiographic, and histologic domains. In practice, ILD classification begins with radiology, when chest imaging is prompted by concerning findings (eg, chronic respiratory symptoms and restrictive pulmonary function testing). Based on their radiologic pattern, ILDs are dichotomized by the presence or absence of a
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Interstitial Lung Disease article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures