Transient Tachypnea Of The Newborn
Article Sections
Introduction
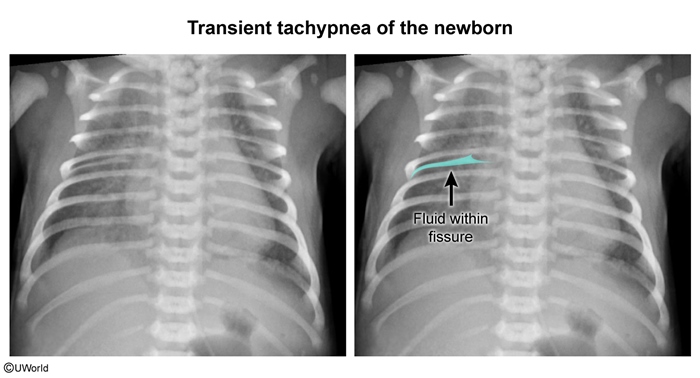
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is a benign, self-limited condition that occurs due to delayed reabsorption of fetal alveolar fluid. It is the most common cause of respiratory distress in late preterm (>34 weeks gestation) and term (>37 weeks gestation) neonates. Patients typically experience respiratory distress (eg, tachypnea, increased work of breathing) shortly after birth.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
In early gestation, fluid is normally secreted into the alveolar space to stretch the parenchyma as it grows and develops. In late gestation, this fluid is actively reabsorbed through sodium channels on alveolar epithelial cells. Reabsorption is most pronounced before and during labor due to surges in catecholamines and other hormones that upregulate sodium channel expression.
In TTN, there is delayed alveolar fluid reabsorption
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Transient Tachypnea Of The Newborn article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages