Cocaine Use Disorder
Article Sections
Introduction
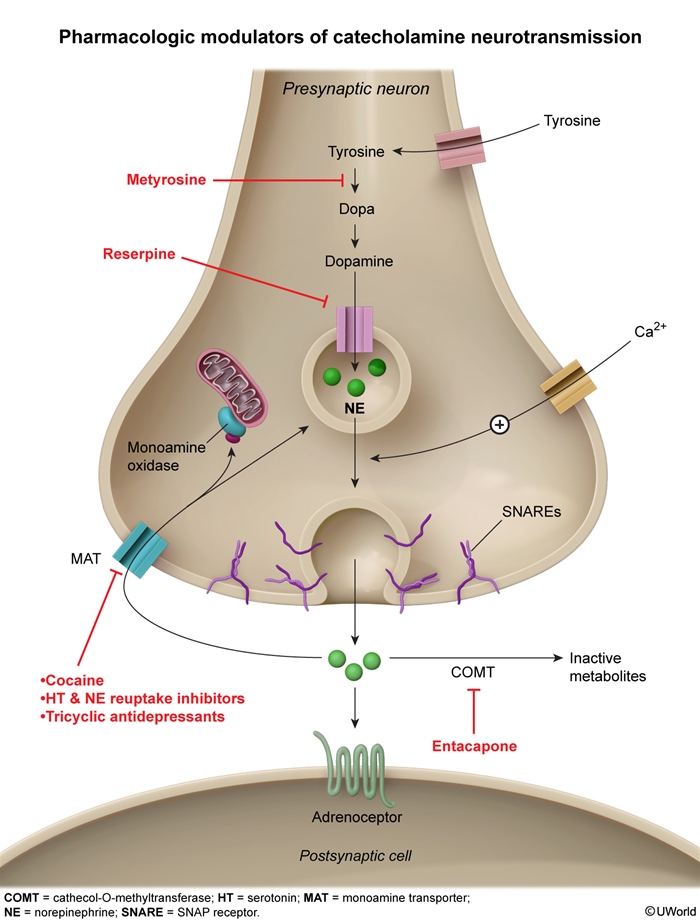
Cocaine use disorder is a chronic, relapsing condition marked by the compulsive use of cocaine despite serious negative physical, psychologic, and social effects. Cocaine, a highly addictive stimulant derived from the coca plant, induces feelings of euphoria and increased energy. However, cocaine intoxication can lead to life-threatening complications, including myocardial infarction, aortic dissection, and intracranial hemorrhage.
Epidemiology and risk factors
Cocaine is exclusively sourced from South America, which may explain its higher prevalence of use in North and South America, as well as in Western and Central Europe. Most people use cocaine occasionally (less than once per week) and in small amounts, but a small percentage of individuals use cocaine daily. Factors that increase the risk for cocaine use include:
- Male sex
- Family history of substance use disorders, particularly involving stimulants
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cocaine Use Disorder article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures