Bulimia Nervosa
Article Sections
Introduction
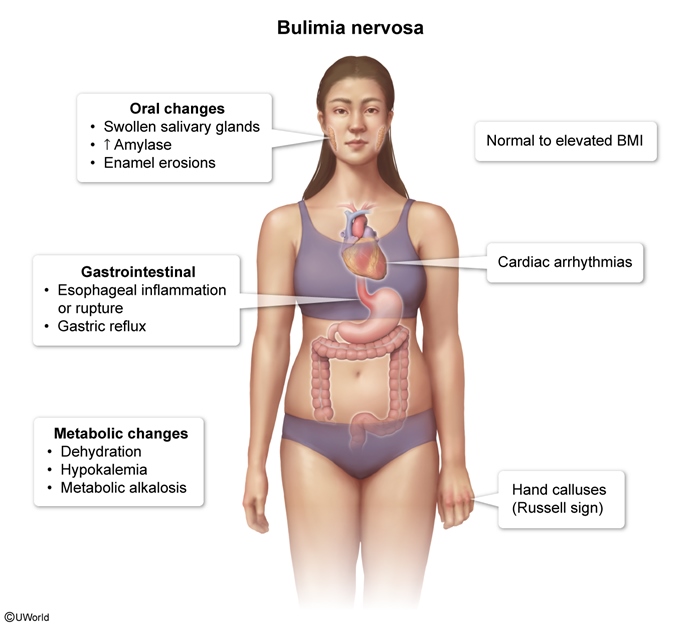
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating, compensatory behaviors to prevent weight gain (eg, self-induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives or diuretics, fasting, excessive exercise), and self-worth that is negatively influenced by body shape/size. Body weight is typically normal or overweight (BMI ≥18.5 kg/m2 and <30 kg/m2). Many patients experience significant shame related to their symptoms and try to conceal binge-eating episodes and purging behaviors.
Epidemiology and risk factors
The estimated lifetime prevalence of bulimia nervosa in middle- to high-income countries is 1%. It is more common in female patients than in male patients (10:1 ratio), and onset is typically during adolescence and young adulthood (age 12-25).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Bulimia Nervosa article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures