Amblyopia
Article Sections
Introduction
Amblyopia is a functional reduction in visual acuity that occurs due to abnormal development of the visual cortex in early childhood. It is one of the most common causes of pediatric visual impairment.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
Normal development of the visual cortex requires appropriately focused visual stimulation from both eyes in early childhood. Therefore, the development of amblyopia is a 2-step process, as follows:
- Step 1: Impaired transmission of a sharply focused image from both eyes due to an underlying ocular defect.
- In deprivation amblyopia, this is due to obstruction of the visual axis (eg, cataract (Figure 1), ptosis, hemangioma).
- In refractive amblyopia, this is due to an uncorrected asymmetric refractive error (eg, myopia, hyperopia (Figure 2)).
- In strabismic amblyopia, abnormal binocular interactions (eg, strabismus (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Amblyopia article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
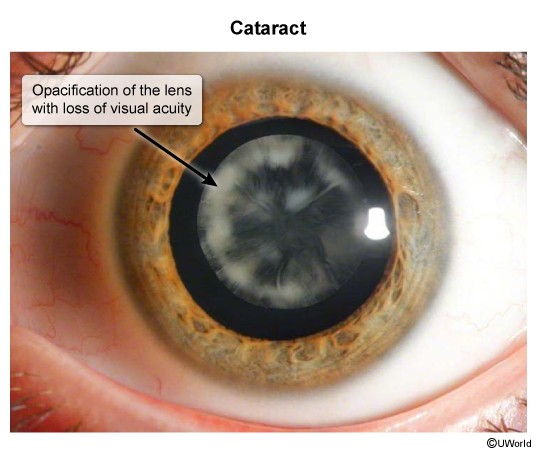
Figure 1
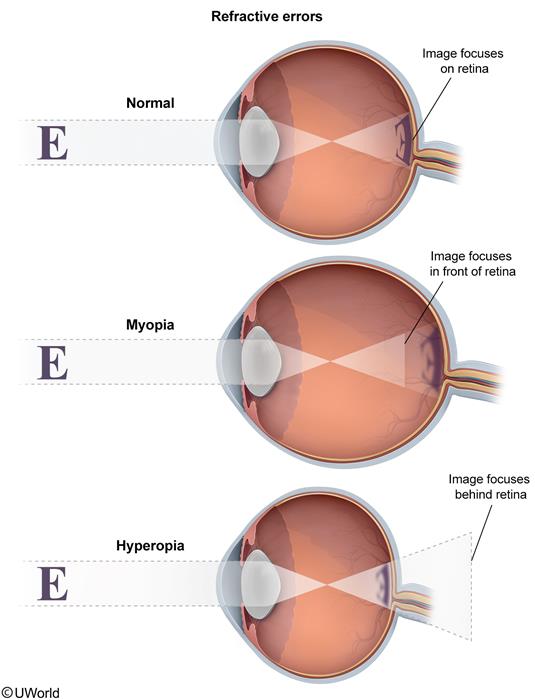
Figure 2
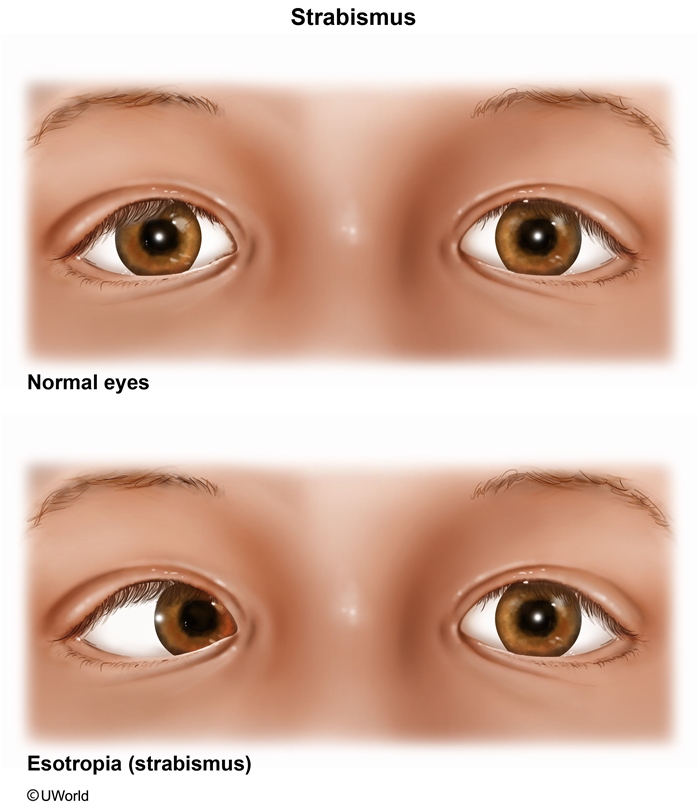
Figure 3
Figure 4
Figure 5

Figure 6