Hordeolum
Article Sections
Introduction
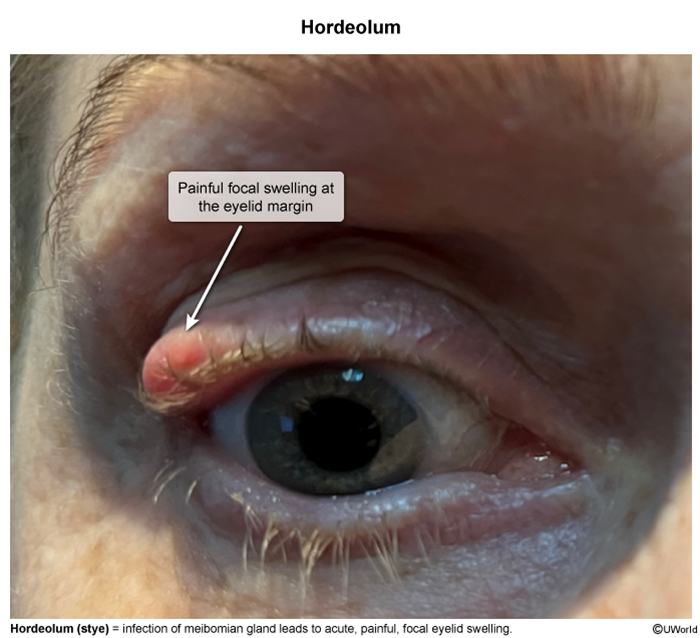
Hordeolum, also known as a stye, is a localized infection or inflammation of the eyelid glands.
Pathophysiology and risk factors
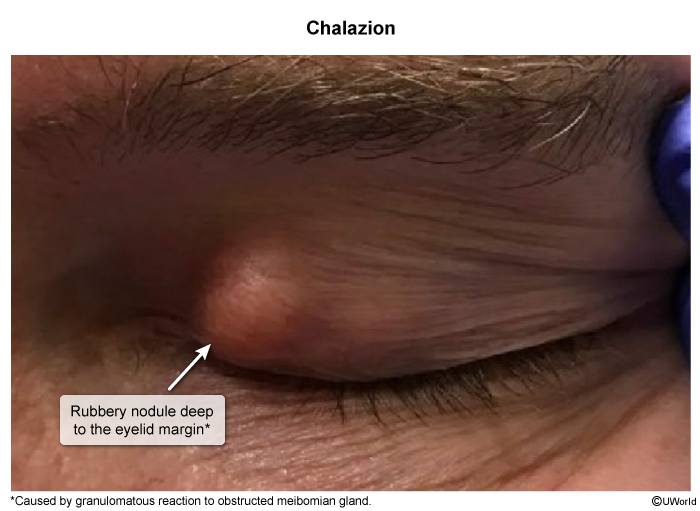
Hordeolum typically arises from the infection of the eyelid glands, particularly the meibomian glands (external hordeolum) or the Zeis glands (internal hordeolum) (Image 1). Staphylococcus aureus is the most frequent causative organism. The inflammation and obstruction of the glandular ducts leads to the accumulation of secretions, resulting in the formation of a painful, erythematous nodule on the eyelid.
Risk factors include poor eyelid hygiene, chronic blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid margin), and skin conditions such as rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, or acne vulgaris.
Clinical presentation
Patients with a hordeolum typically present with a localized, painful swelling on the eyelid; the affected area is often red, swollen, and tender to palpation. An external hordeolum (stye) typically presents as a pustule or abscess at the base of an eyelash follicle, whereas an internal hordeolum may manifest as a deeper, more diffuse swelling within the eyelid.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Hordeolum article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages