Cesarean Delivery
Article Sections
Introduction
Cesarean delivery is a surgical procedure in which a fetus is delivered through an incision in the maternal abdominal wall and uterus. It is one of the most common surgical procedures worldwide, often performed when a vaginal delivery poses a risk to the mother or fetus.
The global cesarean delivery rate varies widely, ranging from <10% in resource-limited settings to >30% in resource-rich settings. Although these are often life-saving procedures, unnecessary cesarean deliveries can lead to maternal and neonatal complications and have implications for future reproductive health and planning.
Indications
A cesarean delivery is performed when it is medically/obstetrically indicated for the well being of mother and/or fetus, or upon patient request.
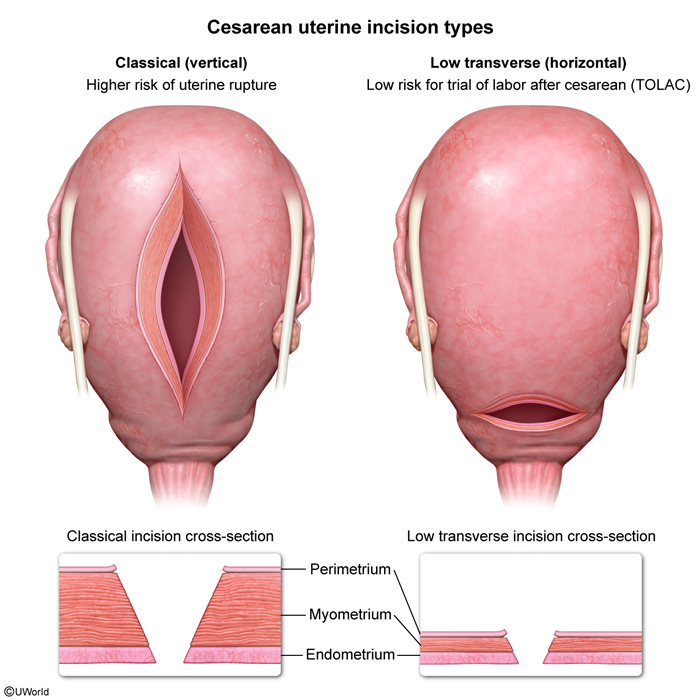
Maternal indications- Prior classical cesarean or extensive transmyometrial uterine surgery (due to risk for uterine rupture).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cesarean Delivery article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures