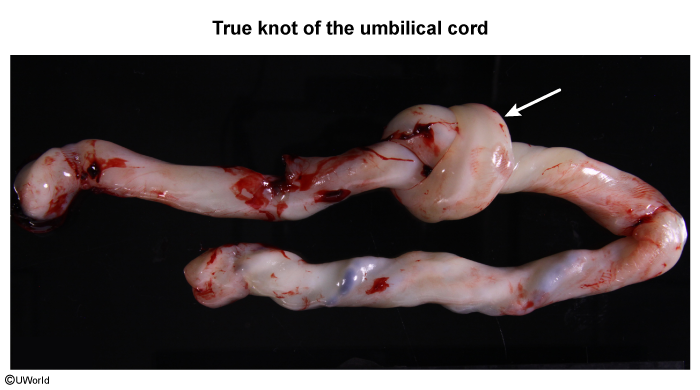
Intrauterine Fetal Demise
Article Sections
Introduction
Intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD), also known as stillbirth, refers to the death of a fetus at ≥20 weeks gestation but prior to the onset of labor. Many possible etiologies exist, including maternal disease, fetal conditions and infection, and placental abnormalities.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
The pathogenesis of IUFD is multifactorial and, despite a thorough evaluation, a cause cannot always be determined. The pathophysiological mechanisms often involve compromised oxygen and nutrient delivery to the fetus, which leads to hypoxia and subsequent fetal death. Interruptions at any point along this pathway can result in IUFD:
- Maternal blood flow to the uterus: May be compromised by vasculopathy (eg, diabetes mellitus, hypertensive disorders) or states of maternal hypoperfusion (eg, diabetic ketoacidosis, hemorrhage, sepsis).
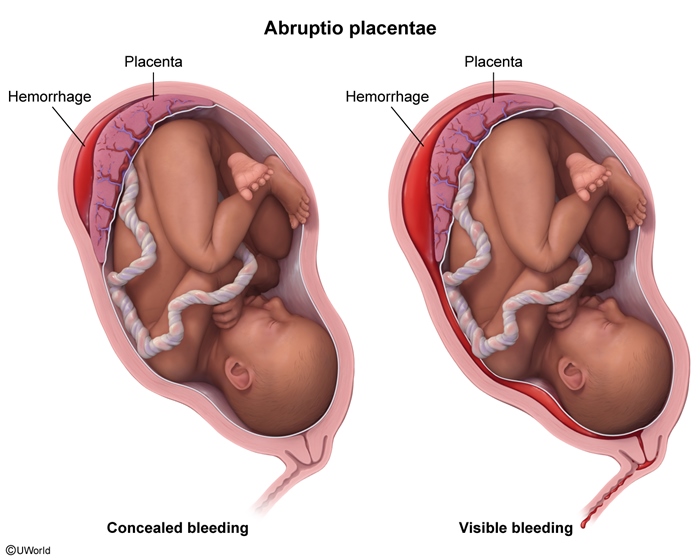
- Placental blood flow: May be compromised by placental abruption (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Intrauterine Fetal Demise article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images