Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
Article Sections
Introduction
Pregnancy losses are common, with up to a third of all pregnancies ending with a miscarriage, and many women experiencing one miscarriage during their reproductive ages. In addition, having a miscarriage between term pregnancies is also common.
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), or recurrent miscarriage, is uncommon and is defined by consecutive pregnancy losses. Clinically, RPL is poorly defined but generally refers to ≥3 consecutive spontaneous abortions at <20 weeks gestation. However, because of the significant psychological impact of pregnancy loss, a work-up is typically begun following ≥2 clinical pregnancies (ie, ultrasound or histopathologic proven pregnancy).
Etiologies
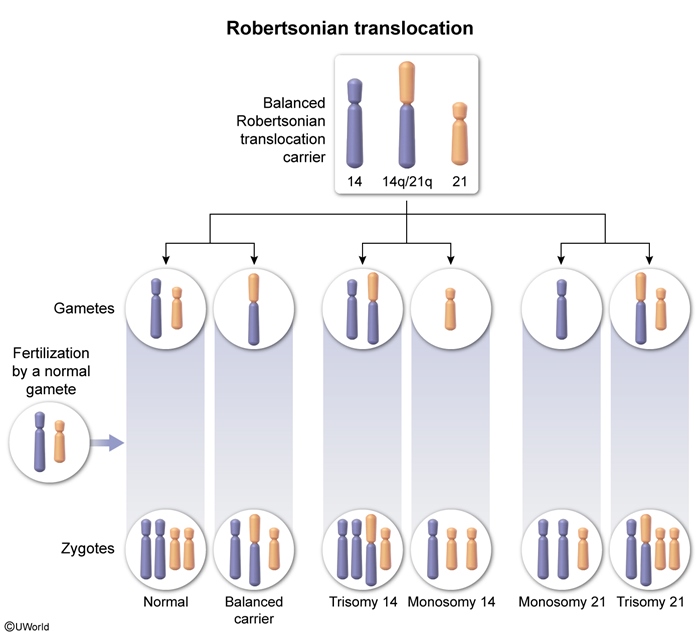
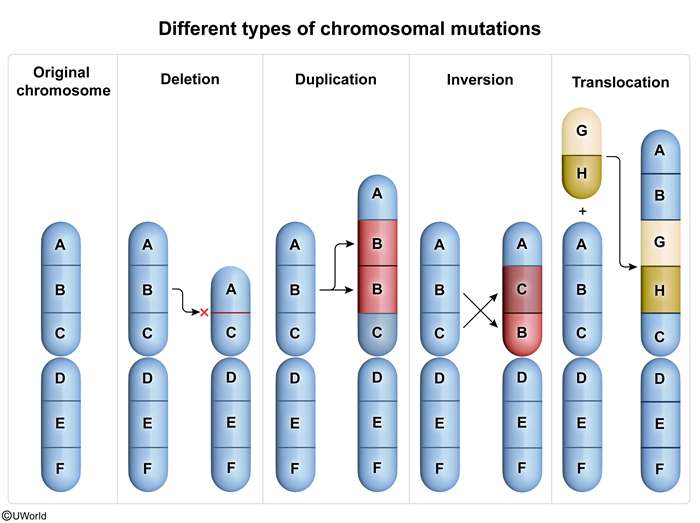
RPL is caused by many different etiologies that may act in isolation or in conjunction with one another. Key mechanisms include:
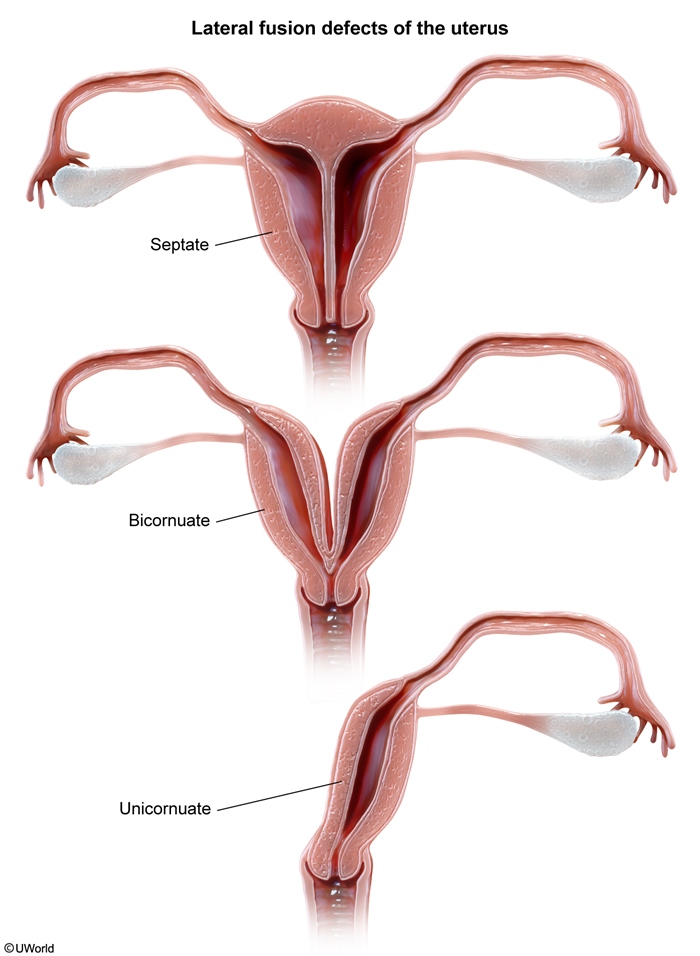
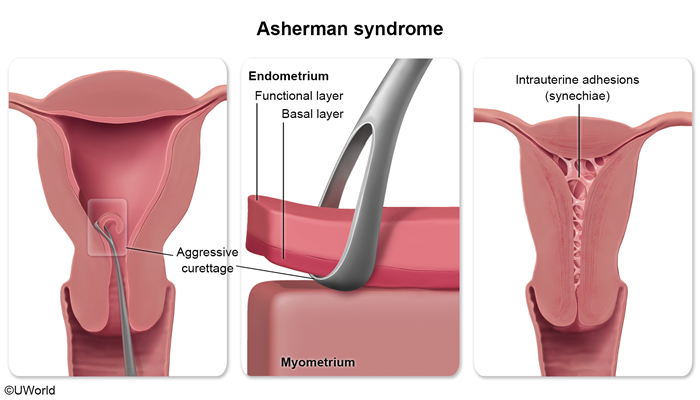
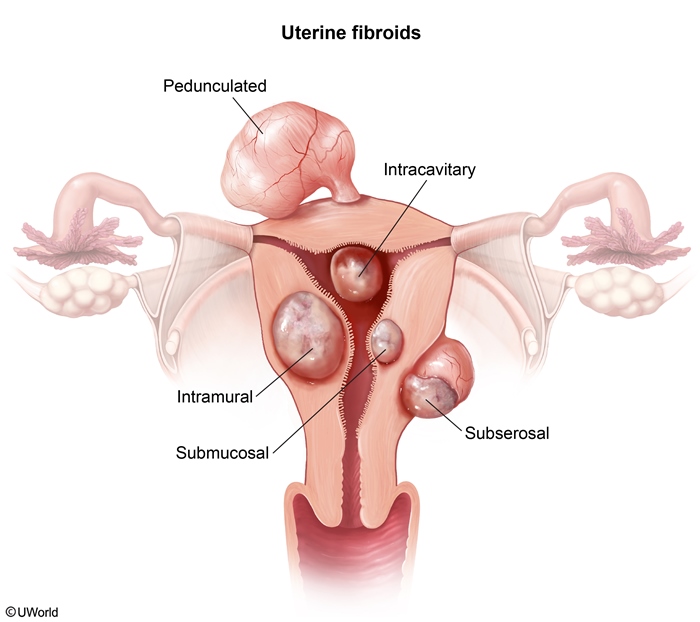
Uterine causesUterine anomalies account for 10% to 50% of RPL cases and are classified as either congenital or acquired.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Recurrent Pregnancy Loss article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures