Preterm Labor
Article Sections
Introduction
Preterm labor (PTL) is characterized by regular, painful uterine contractions resulting in cervical change at <37 weeks gestation. It is the most common cause of spontaneous preterm birth and therefore associated with significant neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Pathogenesis
There are many inciting factors that may result in PTL and spontaneous preterm birth; the best-understood factors include the following:
- Genital tract inflammation and infection: both clinical and subclinical intraamniotic infections are a common cause of PTL because the infection can weaken the amniotic membrane; in addition, genitourinary tract infections (eg, asymptomatic bacteriuria, vaginitis) can activate the maternal inflammatory system, causing uterine contractions.
- Uterine overdistension: excessive mechanical distension of the myometrium (eg, multiple gestation, polyhydramnios) upregulates gap junctions and oxytocin receptors, leading to increased risk of preterm birth.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Preterm Labor article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
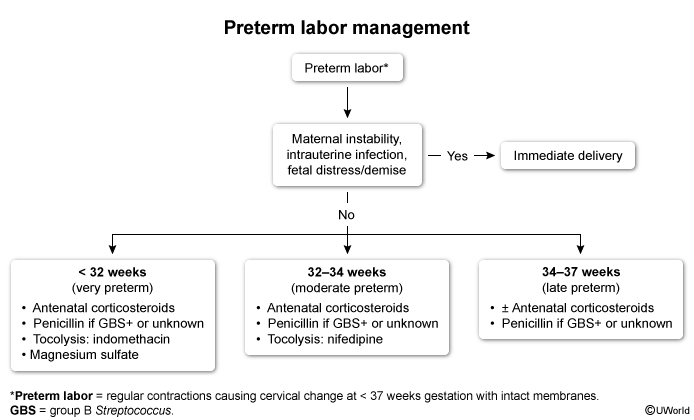
Figure 1
Tables
Table 1
Table 2