Uterine Rupture
Article Sections
Introduction
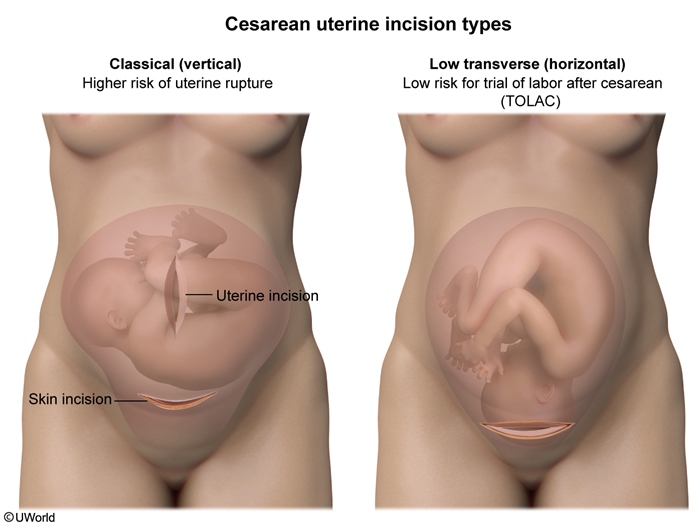
Uterine rupture is an obstetric emergency caused by acute disruption of the uterine wall and bleeding from the rupture site. It typically occurs with uterine contractions during labor and delivery, particularly in patients with a uterine scar (eg, from a prior cesarean delivery).
Pathogenesis and risk factors
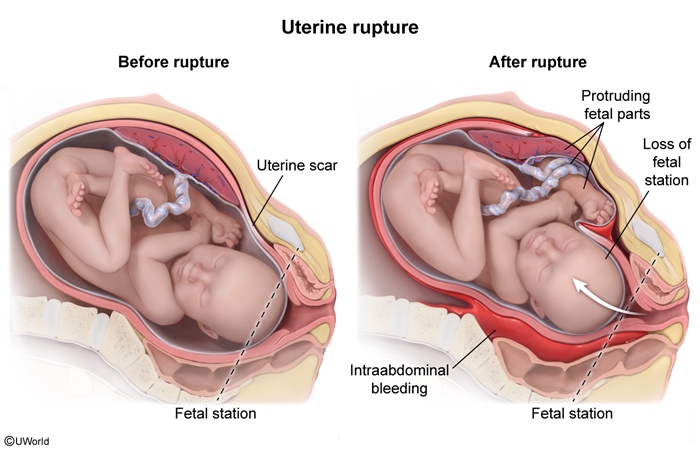
Uterine rupture (Figure 1) most commonly involves acute separation of all the uterine layers, including the serosa (complete rupture); occasionally, the serosa remains intact (ie, incomplete rupture).
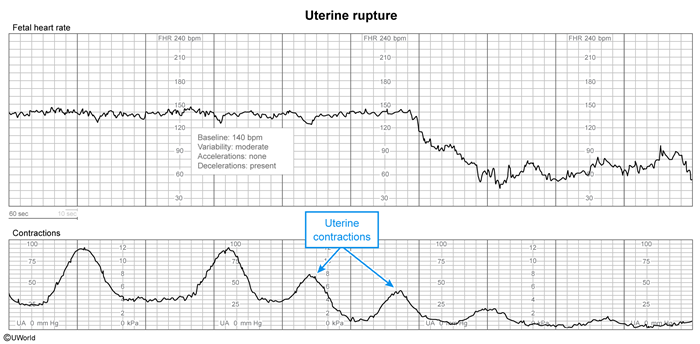
Uterine rupture is defined by its adverse effects on maternal-fetal status. Rupture compromises the integrity of the uterus and causes intraperitoneal bleeding (maternal hemorrhage). It can also precipitate acute placental abruption (separation of the placenta from the uterine wall), which rapidly leads to fetal demise or hypoxia, depending on the extent of the abruption.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Uterine Rupture article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures