Placenta Previa
Article Sections
Introduction
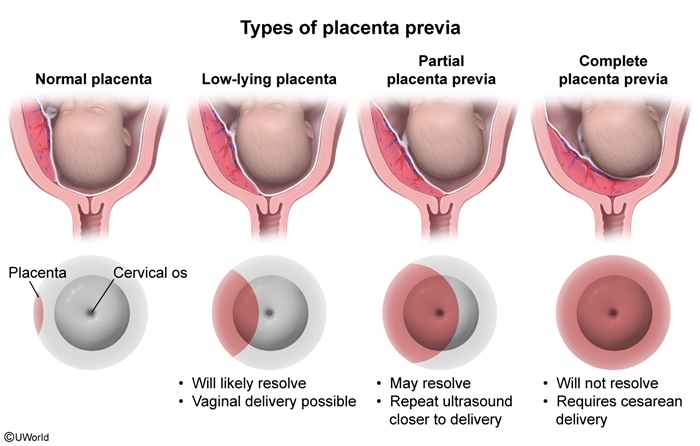
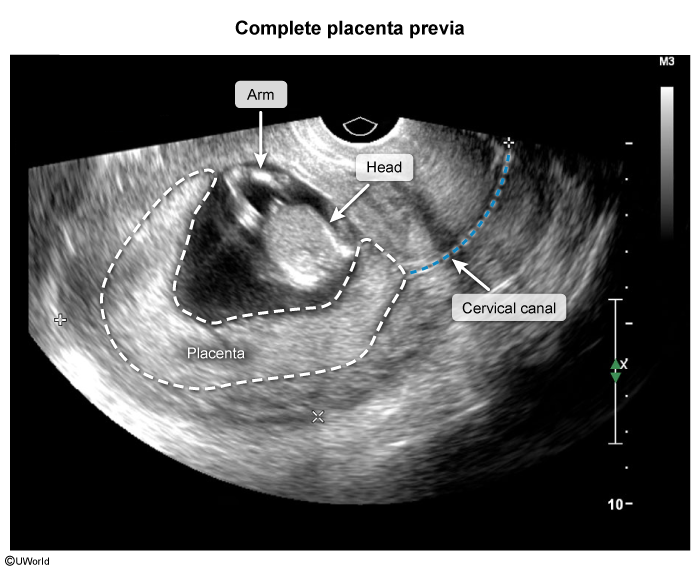
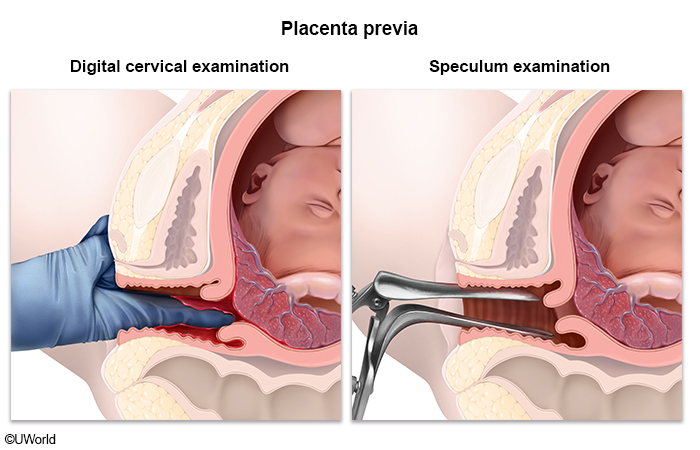
Placenta previa is a condition of pregnancy in which the placenta partially or completely covers the internal os of the cervix, causing a high risk for hemorrhage (due to rupture of placental vessels), particularly during labor and delivery.
Pathogenesis
During pregnancy the placenta normally implants onto the uterine wall, typically somewhere other than the cervix. As the pregnancy progresses, the placenta usually migrates superiorly (toward the fundus and away from the cervix) because the thicker myometrium in the upper uterine cavity is more vascularized (better placental perfusion) than the thinner lower uterine segment. In addition, as the pregnancy progresses, the lower uterine segment naturally expands and thins, which also increases the distance between the placenta and the internal os of the cervix.
In placenta previa (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Placenta Previa article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures