Fetal Heart Rate Tracings
Article Sections
Introduction
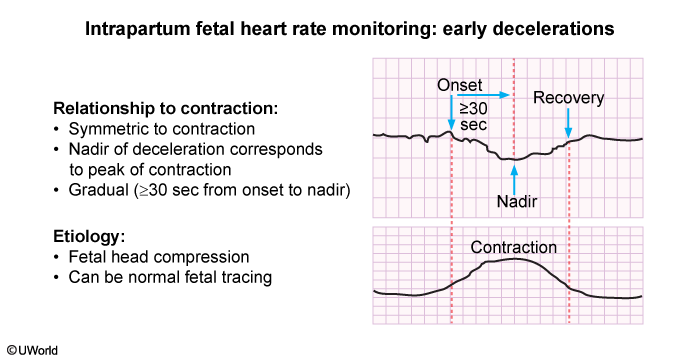
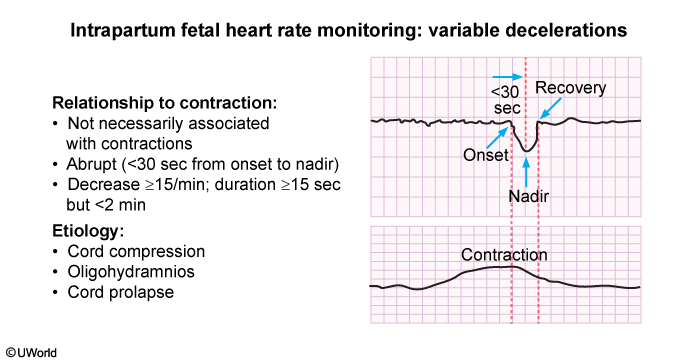
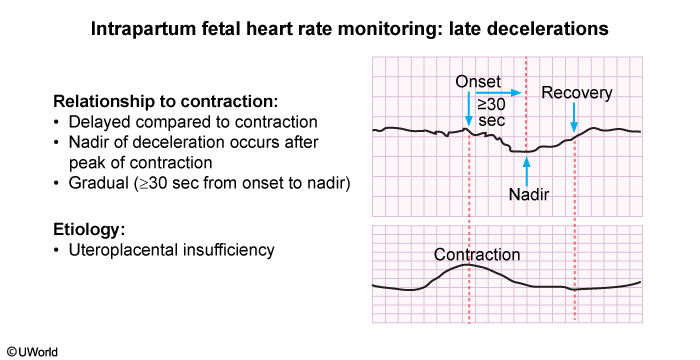
During labor contractions, intermittent reductions in placental blood flow cause transient decreases in fetal oxygenation. Although most fetuses have the ability to compensate for this decrease in fetal oxygenation, some do not have the placental reserve and can develop hypoxemia and eventual metabolic acidosis. Fetal heart rate (FHR) tracings are used to monitor fetal oxygenation status by identifying patterns of the FHR associated with inadequate oxygenation and acidemia.
Components of FHR tracings
FHR tracings are evaluated based on several parameters.
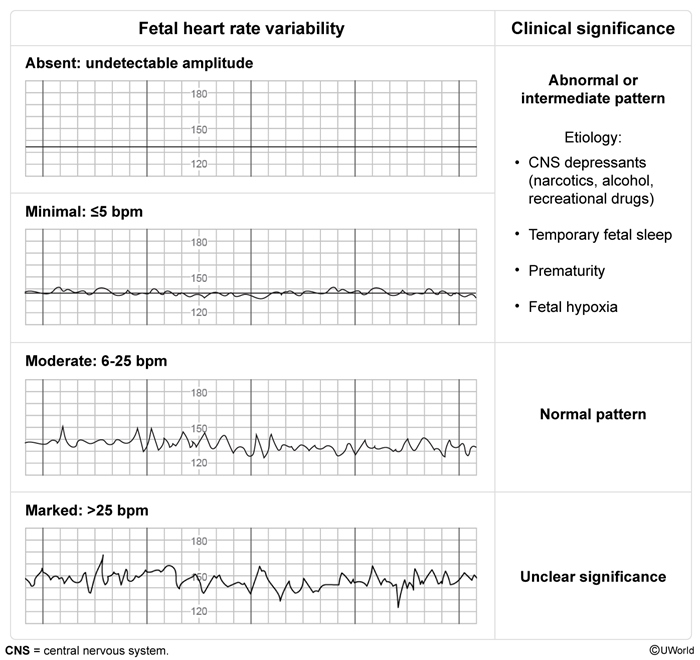
Baseline FHRThe baseline FHR is the average FHR during a 10-minute period, excluding accelerations and decelerations. The baseline FHR is influenced by gestational age, intrinsic cardiac factors, and parasympathetic and sympathetic input, and it can help gauge signs of fetal distress and the stress response:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Fetal Heart Rate Tracings article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures