Preterm Prelabor Rupture Of Membranes
Article Sections
Introduction
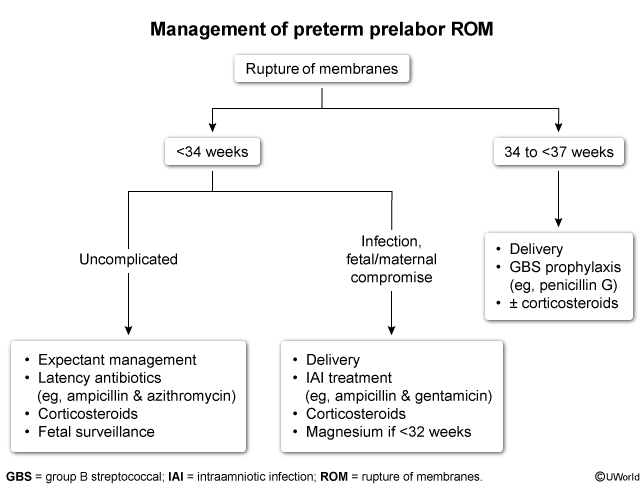
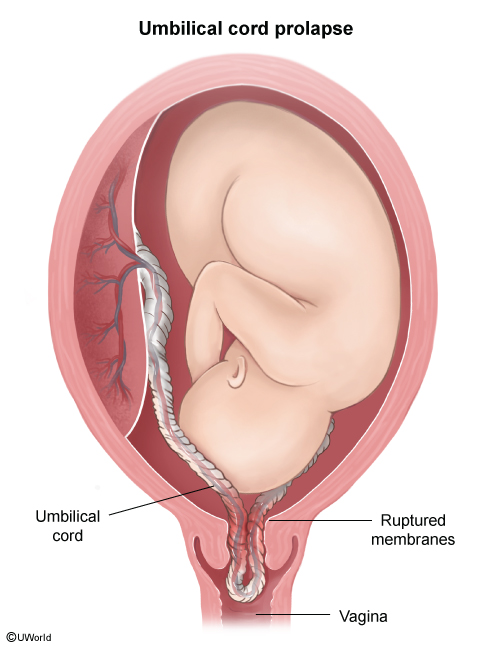
Preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM) is defined as the rupture of the fetal membranes at <37 weeks gestation and prior to the onset of labor (regular contractions with cervical change). PPROM affects about 3% of pregnancies and is associated with various maternal and neonatal complications.
Pathogenesis
The placental membranes arise from the extraembryonic tissues of the zygote and are composed of two layers: the inner amnion (closest to the fetus) and the outer chorion (closest to the endometrium). In early gestation, the layers are distinct, but they soon fuse to form the amniochorionic membranes. The integrity of the membranes is maintained by collagen, laminin, and fibronectin; intact membranes prevent the leakage of amniotic fluid and provide a barrier to protect the fetus from ascending infection from the lower genital tract.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Preterm Prelabor Rupture Of Membranes article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures