Syringomyelia
Article Sections
Introduction
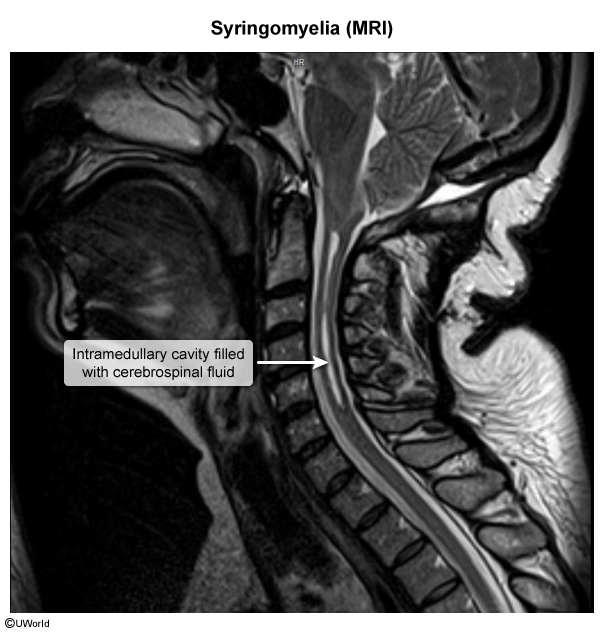
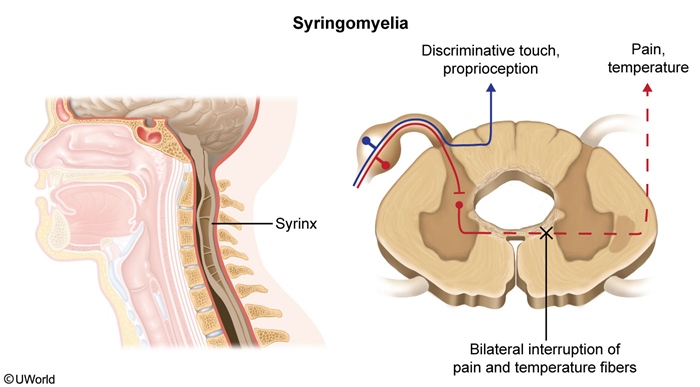
Syringomyelia is a chronic neurologic disorder characterized by the formation of a fluid-filled cyst (syrinx) within the spinal cord; this cyst can expand over time and cause progressive neurologic dysfunction. The condition is often associated with Chiari malformation type I (CM-I) and can lead to chronic pain, sensory loss, and motor dysfunction.
Neuroanatomy and pathogenesis
Syringomyelia is a disorder in which a fluid-filled cavity (ie, syrinx) forms within the spinal cord (Figure 1). The syrinx may represent dilation of the central canal or a separate cavity within the spinal parenchyma and is usually located within the cervical or thoracic spine. The cavity can enlarge over time and destroy adjacent portions of the spinal cord. The areas most commonly damaged are:
- The
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Syringomyelia article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images