Cervical Artery Dissection: Carotid And Vertebral Artery Dissection
Article Sections
Introduction
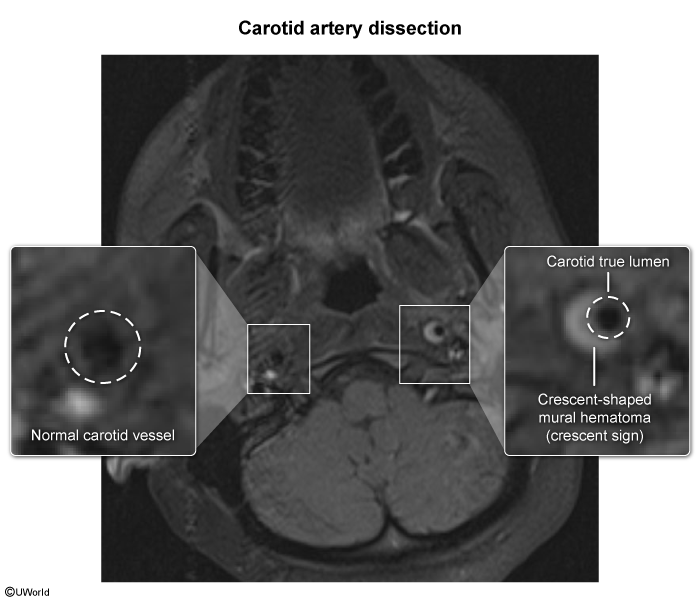
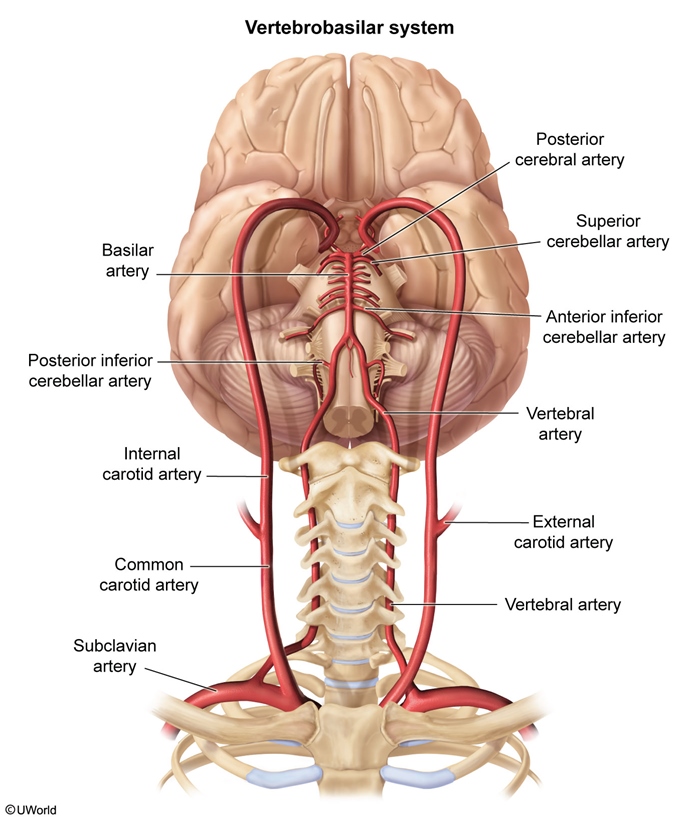
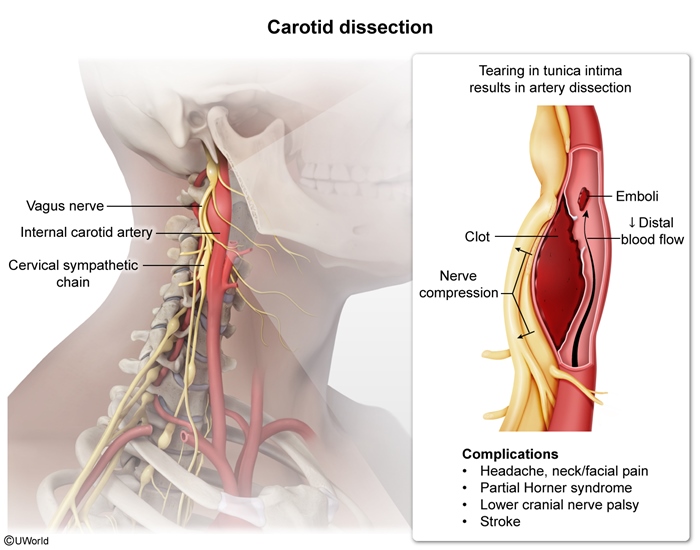
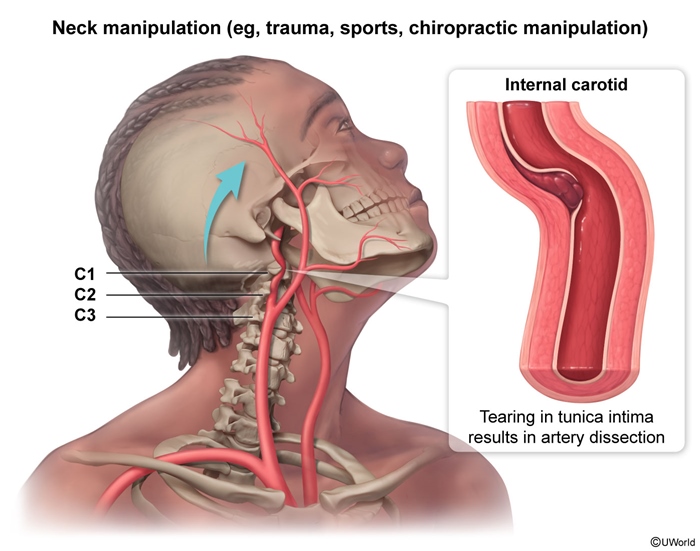
Cervical artery dissections refer to the rupture of the intimal layer of the carotid or vertebral arteries in the neck, leading to the formation of an intramural hematoma. This hematoma can obstruct blood flow or cause thromboembolism, potentially resulting in neurologic deficits due to compromised cerebral perfusion. These dissections are significant causes of ischemic stroke and account for approximately 25% of strokes in younger people. The condition typically results from trauma, which can be major (eg, motor vehicle collision) or minor (eg, cervical manipulation). Some cases without a clear cause are called "spontaneous," but it may be that the mechanical trigger is simply not identified. Connective tissue disorders and other underlying vulnerabilities (eg, hypertension, smoking) put the patient at greater risk. Early recognition and antithrombotic therapy reduce the risk for complications (eg, stroke).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Cervical Artery Dissection: Carotid And Vertebral Artery Dissection article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images