Facial Palsy
Article Sections
Introduction
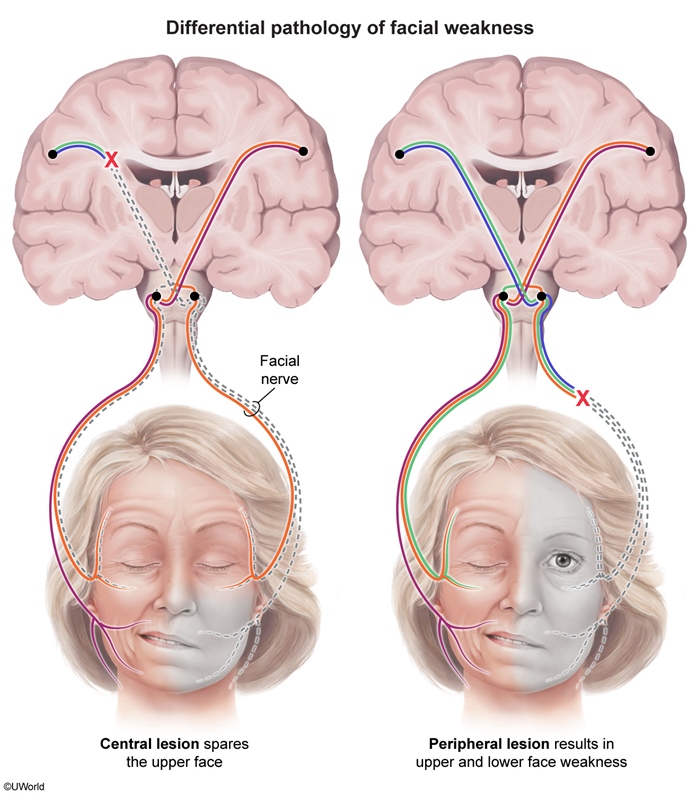
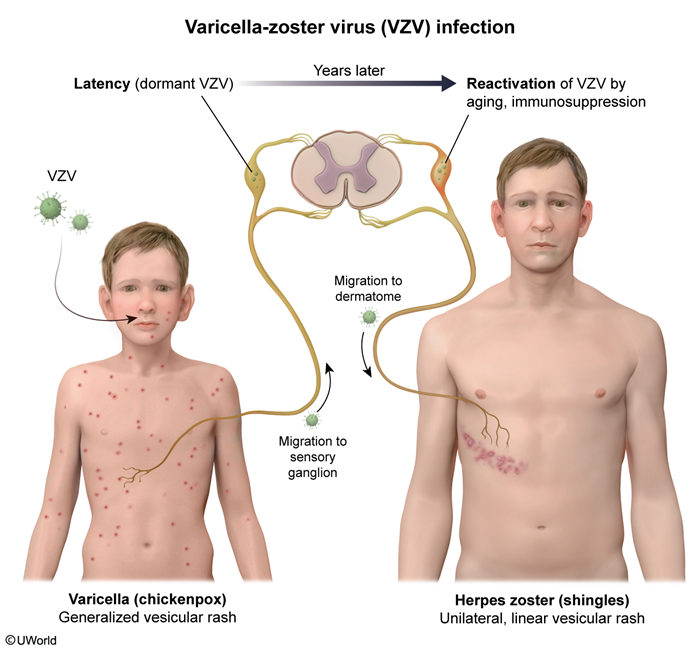
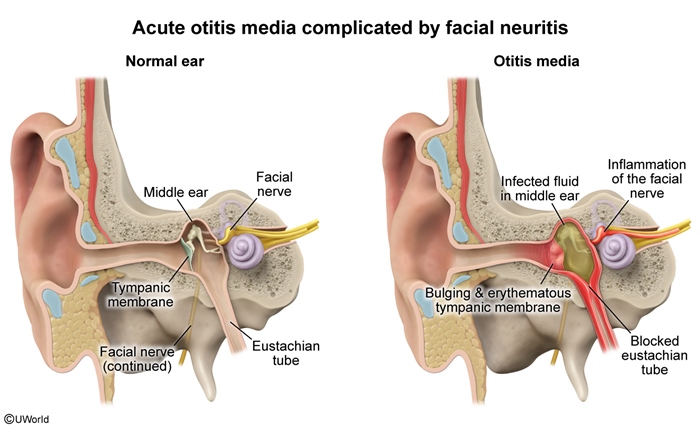
Facial palsy is a condition characterized by weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles. It can result from damage to the facial nerve (CN VII), either centrally or peripherally. Although it is most commonly idiopathic (Bell palsy), this condition is a diagnosis of exclusion because facial palsy can also be caused by treatable infections (eg, herpes zoster, Lyme disease) or tumors or inflammatory conditions (which should be diagnosed quickly to improve prognosis). It can also be caused by trauma, which would necessitate evaluation for additional, more serious injuries (eg, intracranial bleeding).
Pathophysiology and clinical presentation
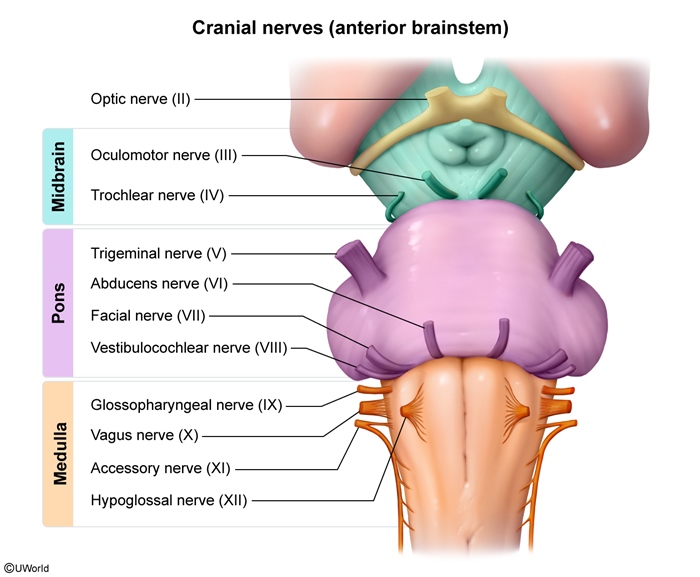
Voluntary facial movement is initiated by the motor cortex (located in the frontal lobe), which delivers input to the facial nerve (CN VII). This nerve originates in the pontomedullary junction (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Facial Palsy article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures