Vascular Dementia
Article Sections
Introduction
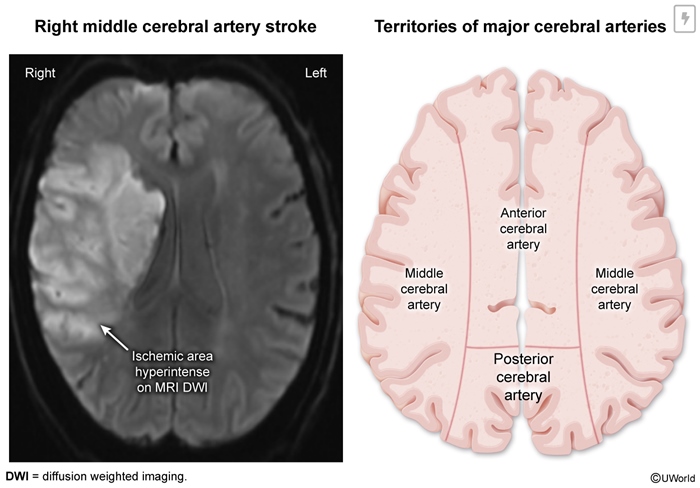
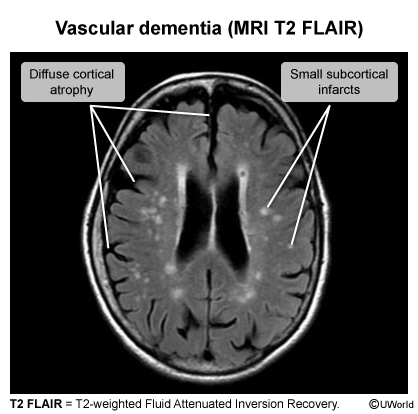
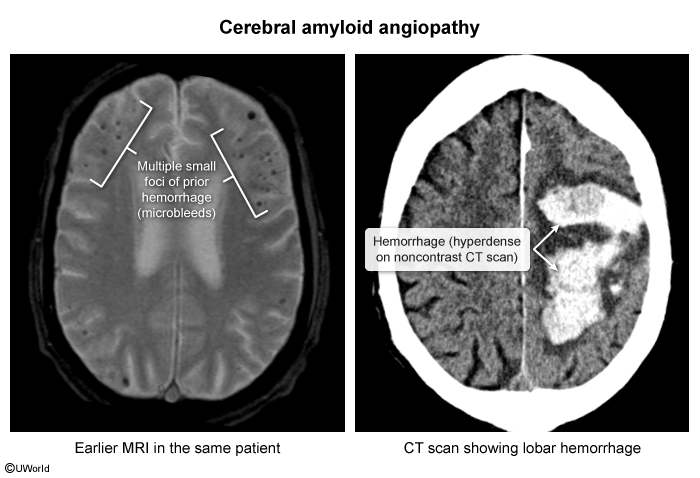
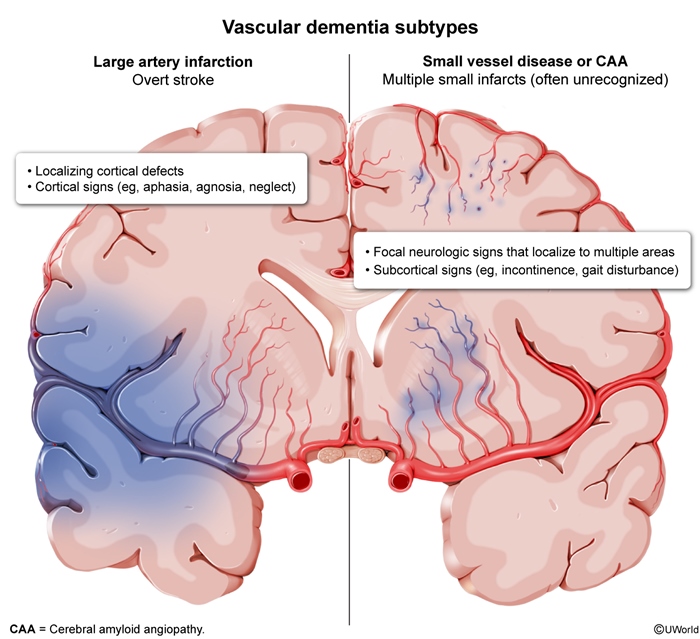
Vascular dementia (VaD) describes cognitive impairment resulting from any cause of vascular brain injury (typically infarction or hemorrhage) and is most commonly due to large artery stroke, small vessel disease, or cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Epidemiology
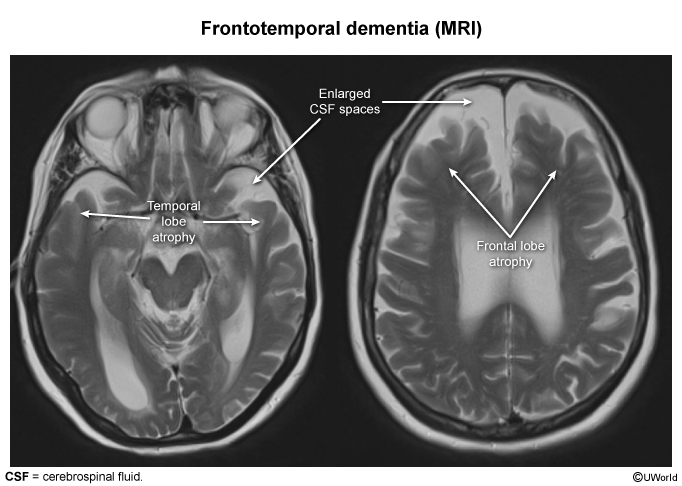
VaD is second only to Alzheimer disease (AD) as the primary cause of dementia. VaD in isolation accounts for approximately 10% of dementia cases, but it commonly (~40% of cases) coexists with other dementia causes (ie, "mixed dementia," particularly VaD-AD). This underscores the significant overlap between VaD and AD with regard to both risk factors and pathogenesis.
Risk factors
Because VaD typically results from stroke, the risk factors are the same for both and include:
- Advancing age
- Previous stroke
- Vascular risk factors including hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and smoking
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Vascular Dementia article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images