Pediatric Brain Tumors
Article Sections
Introduction
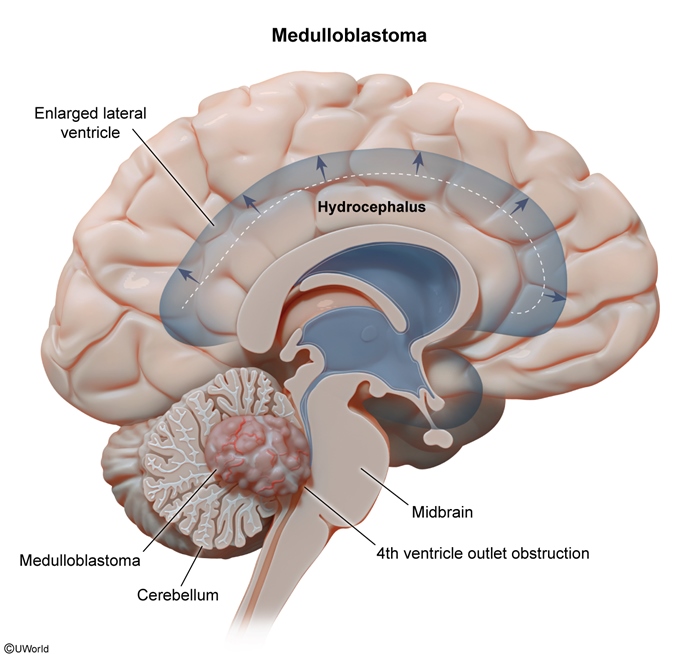
CNS tumors are the second most common pediatric malignancies after leukemia and the most common pediatric solid tumors. The most frequent types of primary brain tumors in children differ in type and location from those in adults. The general pathophysiology, epidemiology/risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management of primary brain tumors are discussed in more detail in a separate article.
Pathophysiology
Brain tumors can be classified according to their cell type of origin. The brain is composed of 2 major cell types: neurons and glial cells. Neurons, which transmit information throughout the brain using electrical signals and chemical messengers, rarely form tumors. Tumors more commonly originate from glial cells, which significantly outnumber neurons and normally provide support to maintain the health of the nervous system. There are 3 main types of glial cells:
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Pediatric Brain Tumors article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images