Transverse Myelitis
Article Sections
Introduction
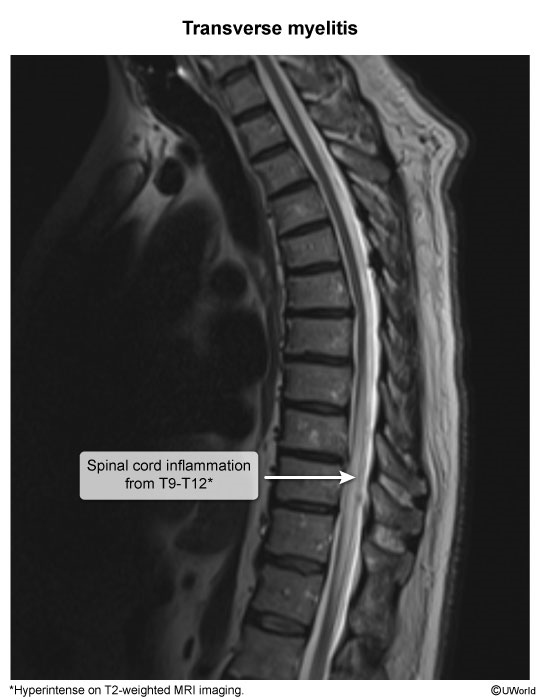
Transverse myelitis (TM) is an inflammatory disorder of the spinal cord characterized by rapid onset of neurologic symptoms.
Pathophysiology
TM is an immune-mediated disorder characterized by infiltration of inflammatory cells into a segment of the spinal cord. This leads to neuron and oligodendrocyte cell death and demyelination, which causes neurologic impairment in a characteristic pattern.
Epidemiology and risk factors
Most cases of TM follow a recent infection (eg, gastroenteritis, upper respiratory infection). The condition is also associated with various autoimmune disorders, including multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, and systemic diseases (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus). TM has a bimodal peak, with most cases occurring in the teens and 30s.
Clinical presentation
Patients with TM typically have acute-onset, rapidly progressive myelopathy that localizes to ≥1 contiguous spinal cord segments
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Transverse Myelitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages