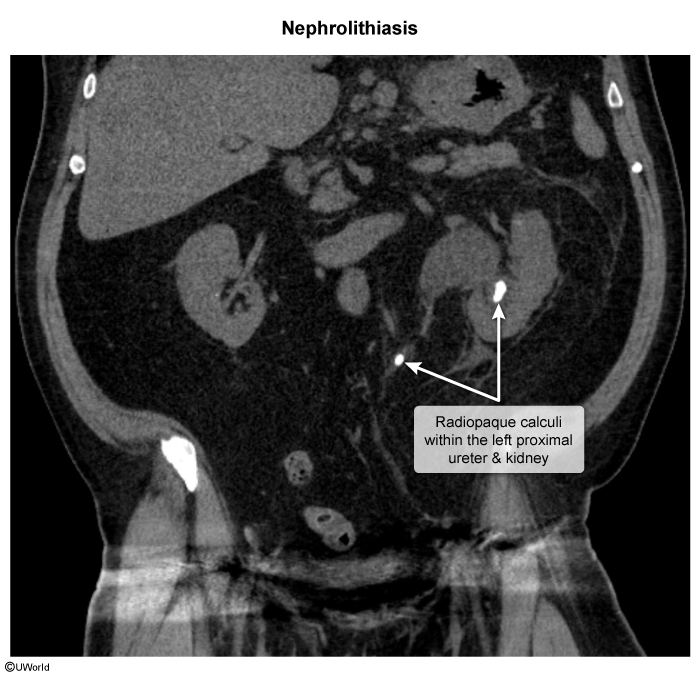
Nephrolithiasis
Article Sections
Introduction
Nephrolithiasis, commonly known as kidney stones, is a prevalent urological disorder characterized by the formation of solid concretions in the kidneys. Nephrolithiasis occurs more frequently in males than in females by a ratio of 3:1, although this gap has been narrowing in recent years. The peak age of onset for nephrolithiasis is between age 20-50. There has been increased incidence over the past several years, which is attributed to various factors including dietary changes and increasing obesity rates. Recurrence rates are high if preventive measures are not taken, with about 50% of individuals experiencing a subsequent stone within 5-10 years of their first episode.
Pathophysiology
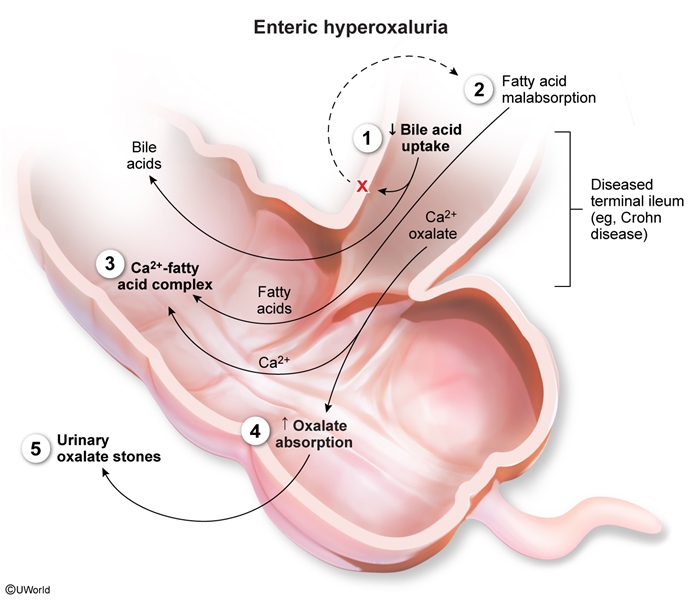
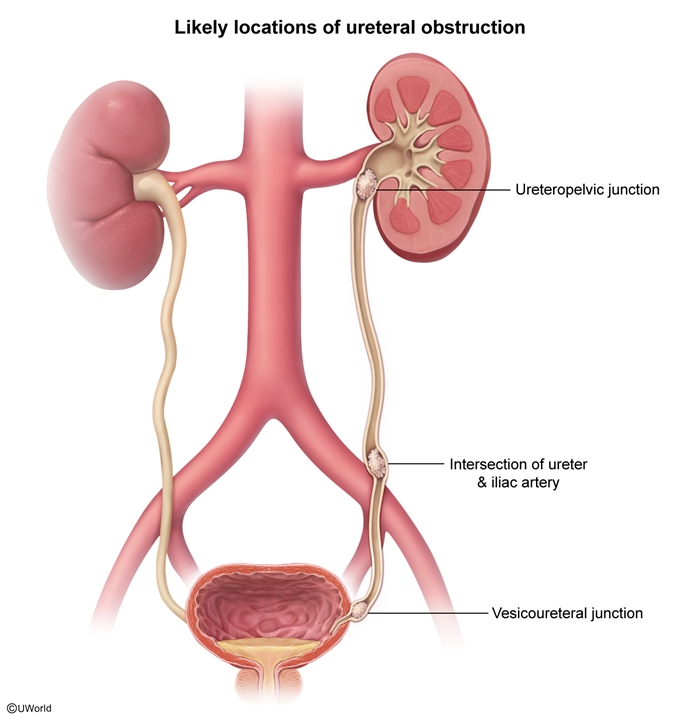
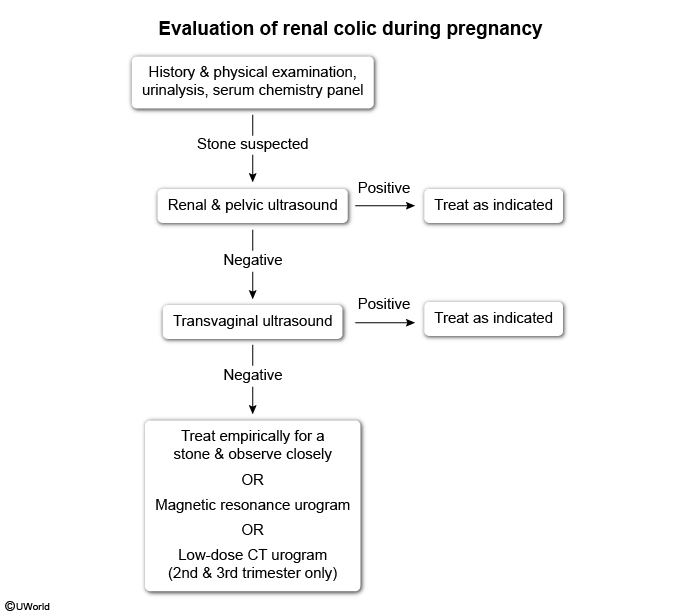
Kidney stones form when an imbalance exists between stone-promoting and stone-inhibiting factors in the urinary system. This process typically involves several stages.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Nephrolithiasis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images