Orchitis
Article Sections
Introduction
Orchitis refers to the inflammation of one or both testicles. It is typically observed with bacterial epididymitis (ie, epididymoorchitis), but can also result from viral infections (eg, mumps). The condition presents with testicular pain, tenderness, and swelling. Diagnosis is mostly clinical, but testicular ultrasonography is often used to rule out conditions with similar presentations (eg, testicular torsion).
Pathogenesis
Orchitis typically results from a viral or bacterial infection:
- Viral: Mumps is the most common cause of viral orchitis (Table 1). Although mumps infection is usually self-limited, unvaccinated patients are at increased risk for complications, including orchitis and aseptic meningitis (Figure 1). Less common causes of viral orchitis include rubella virus, Coxsackievirus, varicella-zoster virus, and cytomegalovirus.
- Bacterial: Most cases of bacterial orchitis occur in patients with concurrent epididymitis, causing
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Orchitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
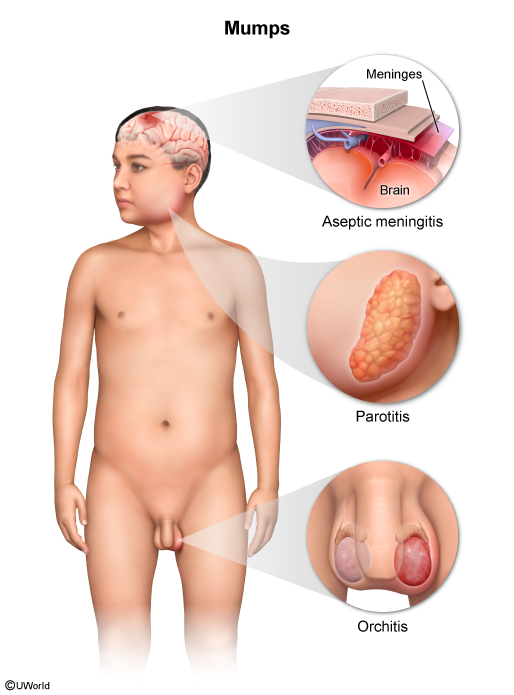
Figure 1
Tables
Table 1