Penile Fracture
Article Sections
Introduction
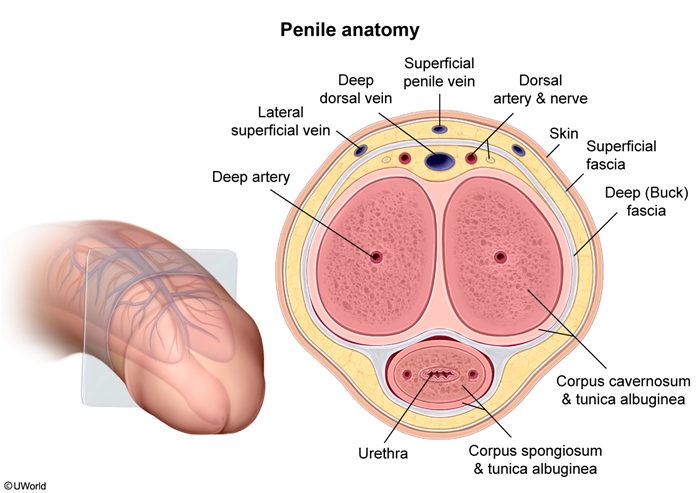
Penile fracture is a relatively uncommon but serious urological emergency characterized by traumatic rupture of the tunica albuginea that surrounds the corpus cavernosum (Figure 1). It typically occurs from blunt force to an erect penis, most often during vigorous sexual intercourse. Symptoms include sudden loss of erection, severe penile pain, and edema and ecchymosis of the penis. Prompt surgical intervention to repair the tunica albuginea is necessary to avoid complications such as erectile dysfunction.
Pathophysiology
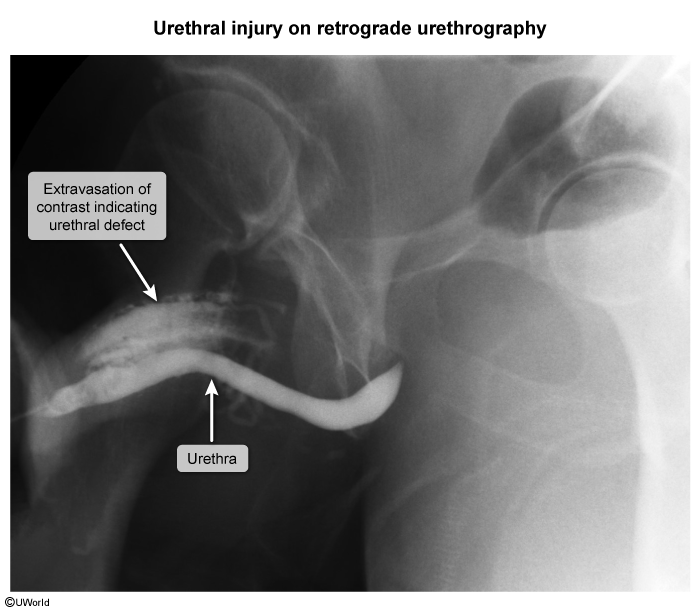
Penile fracture typically occurs during sexual intercourse when the penis slips out of the vagina and is accidentally and forcefully thrust against the perineum or pelvic bone. The excessive bending force tears the tunica albuginea, which is the thick, fibrous sheath that envelops the blood-filled corpus cavernosum. Sheath rupture leads to immediate detumescence (loss of erection) and hematoma formation within the penis. Concomitant urethral injury may also occur due to the close proximity of the urethra to the corpus spongiosum.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Penile Fracture article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images