Epididymitis
Article Sections
Introduction
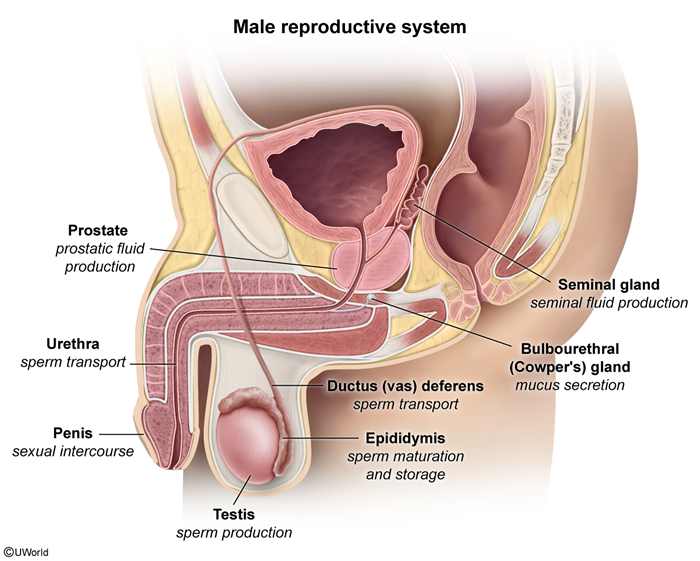
Acute epididymitis is a common cause of acute scrotal pain characterized by inflammation of the epididymis, the tubular structure located on the posterior aspect of each testicle (Figure 1). Acute epididymitis is most often caused by bacterial organisms that ascend from the urethra; the identity of the pathogen varies by patient age. Typical clinical findings include the gradual onset of unilateral testicular pain and swelling and epididymal tenderness on examination. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment.
Pathophysiology
Most cases of epididymitis occur when genitourinary pathogens travel in a retrograde fashion from the urethra to the vas deferens and into the epididymis. The most likely bacterial organisms vary by patient age and risk factors.
- Men age <35: Most cases of epididymitis are caused by sexually transmitted infections, specifically
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Epididymitis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures