Trachoma
Article Sections
Introduction
Trachoma is a chronic keratoconjunctivitis caused by infection with Chlamydia trachomatis serovars A, B, and C. It is the leading infectious cause of blindness worldwide and is particularly prevalent in resource-limited areas in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and parts of Latin America. It is spread from eye to eye by contact with objects (eg, fingers, fomites, flies) contaminated by infectious ocular or nasal secretions.
Pathogenesis
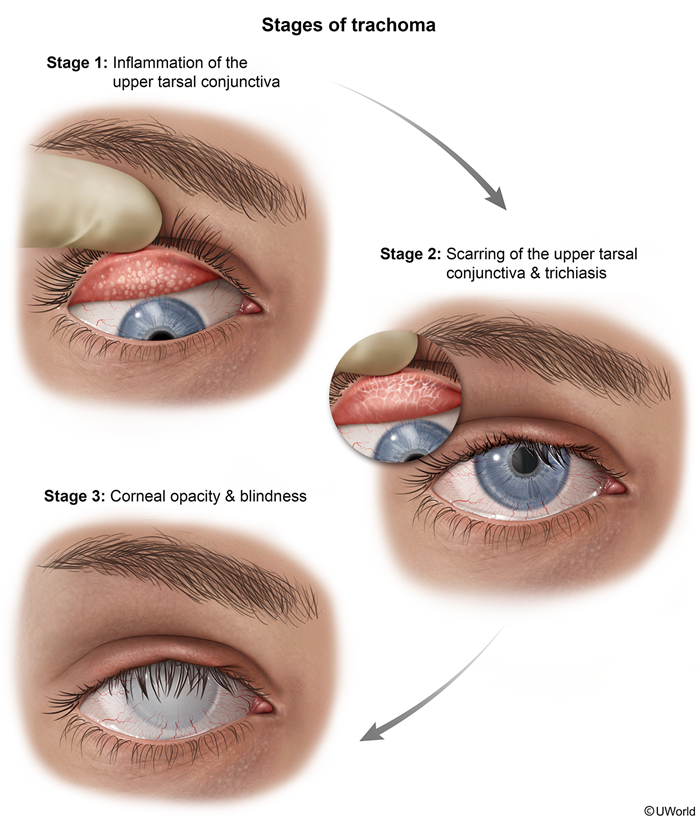
Trachoma results from repeated infection with C trachomatis serovars A-C, which triggers a chronic inflammatory response in the conjunctivae. Over time, this inflammation leads to scarring, in-turned eyelashes (trichiasis), and corneal damage, which can result in blindness.
The pathogenesis of trachoma occurs in 2 main phases (Figure 1):
- Active infection (follicular and intense inflammation): This phase is most common in children and characterized by
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Trachoma article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures