Pinworm Infection (Enterobiasis)
Article Sections
Introduction
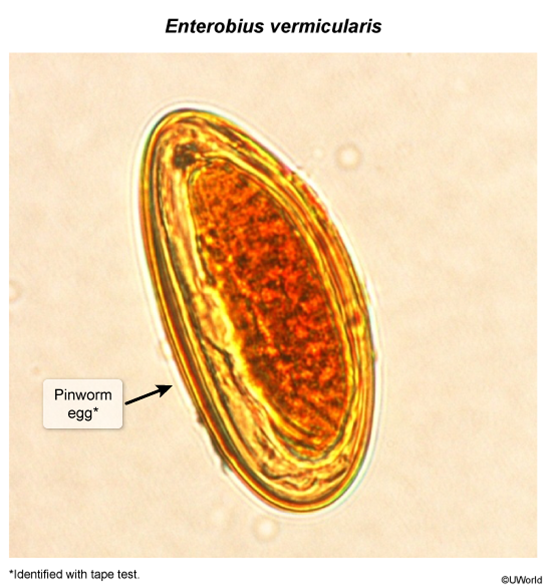
Pinworm infection, or enterobiasis, is a common, highly transmissible intestinal helminth infection that primarily affects school-aged children. Transmission is via ingestion of eggs, and the hallmark symptom is nocturnal perianal itching. Diagnosis is via visualization of worms or eggs.
Pathogenesis
Enterobiasis, caused by the pinworm Enterobius vermicularis, is a common helminth infection in school-aged children.
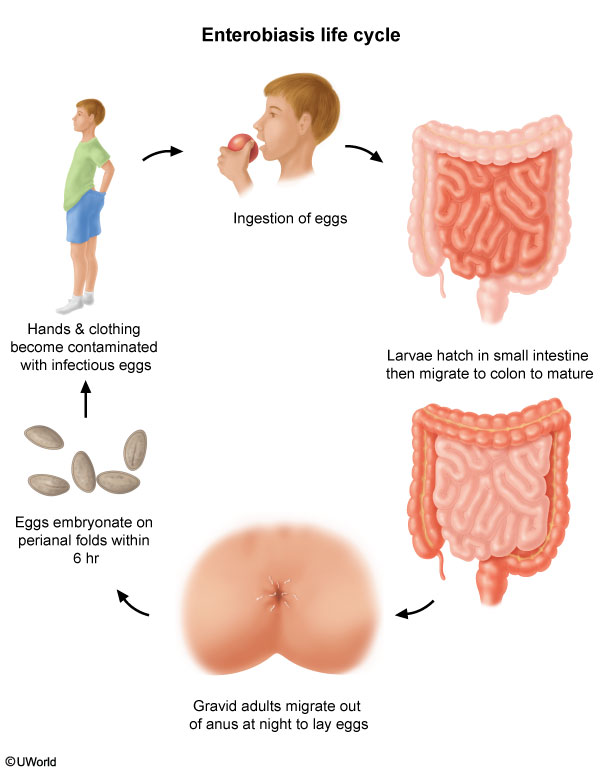
Transmission occurs via ingestion of eggs, typically from unwashed hands after the handling of contaminated food or objects (eg, bedding, clothing) (Figure 1). The larvae develop into adult worms within the distal small intestine and colon. At night, female worms migrate through the rectum and deposit eggs in the perianal region; eggs and worms in the perianal area cause an inflammatory reaction, resulting in perianal itching (pruritus ani). Mature pinworms can also spread to the vagina and cause vulvovaginitis. Scratching contaminates the hands, and eggs can be ingested by the same individual or spread to others.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Pinworm Infection (Enterobiasis) article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images