Antimicrobials: Antifungals
Article Sections
Introduction
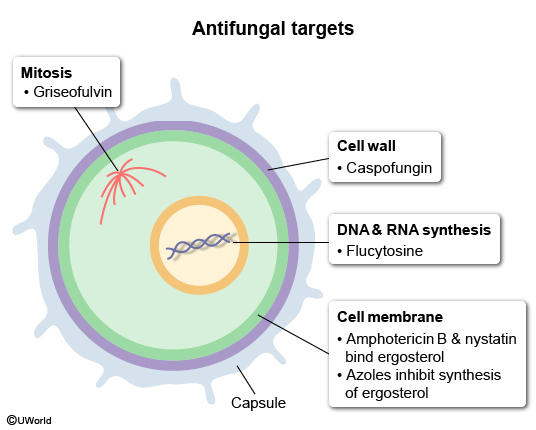
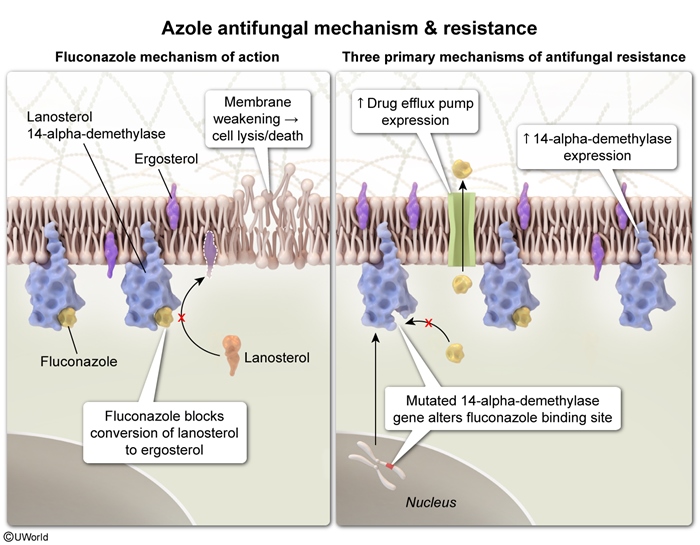
Antifungal agents represent approximately 20 individual drugs across 6 classes. The first half of this article presents the major classes of antifungals, including their mechanisms of action, spectra of activity, major indications, and important adverse effects. The second half provides a general framework for antifungal selection.
Fungi and antifungals
The medically important fungi (Table 1) can be categorized as:
- Yeasts (eg, Candida, Cryptococcus).
- Molds (eg, Aspergillus, Mucor, dermatophytes).
- Dimorphic (mold in environment, yeast in host) (eg, Histoplasma, Blastomyces, Coccidioides).
The distinction between yeasts and molds is relevant primarily for histopathologic identification (eg, observing branching hyphae in molds) but plays a lesser role in antifungal selection. Instead, the choice of antifungal is guided primarily by the clinical category of infection (eg, skin and superficial infections, systemic and invasive infections), as described later.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Antimicrobials: Antifungals article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures