Infectious Urethritis
Article Sections
Introduction
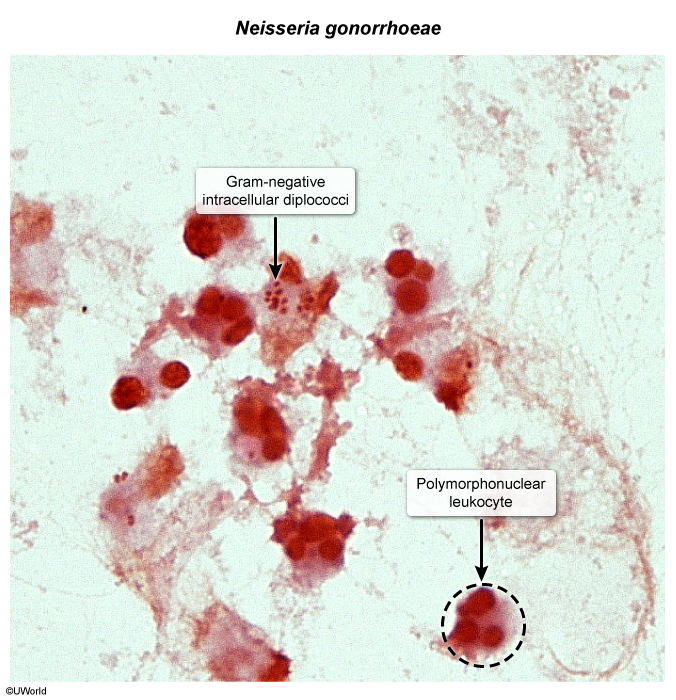
Infectious urethritis is inflammation of the urethra caused by sexually transmitted pathogens, most commonly Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis. It is most prevalent in young, sexually active individuals and typically presents with dysuria and urethral discharge. Although urethritis occurs in males and females, females typically present symptomatically with cervicitis (eg, vaginal discharge) or pelvic inflammatory disease (eg, pelvic pain) rather than isolated urethritis.
This article will focus mainly on urethritis in men (Table 1).
Pathogenesis
Infectious urethritis occurs when viral or bacterial pathogens are introduced into the urethra through unprotected sexual contact. These organisms invade the urethral mucosa and trigger an inflammatory response within the epithelium, resulting in urethral discomfort (eg, dysuria) and discharge.
There are 2 major categories of infectious urethritis, gonococcal and nongonococcal (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Infectious Urethritis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessImages