Surgical Site Infections
Article Sections
Introduction
Surgical site infections (SSIs) are infections that occur near a surgical site ≤30 days after surgery (or within 90 days if prosthetic material was implanted) and are a common cause of postoperative fever (Figure 1). SSIs may involve the incision or any area that was manipulated during the procedure and are a common postoperative complication that contributes to increased morbidity, prolonged hospital stays, and higher health care costs.
Surgical site infections are classified based on the tissue involved:
- Superficial incisional infections involve the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
- Deep incisional infections involve fascia and muscle.
- Organ/deep space infections involve any space deeper than the fascia/muscle (eg, intraabdominal abscess, joint infection, spinal abscess, endometritis).
- Necrotizing soft tissue infections involve the skin, subcutaneous tissue, fascia, and muscle, and are life-threatening.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Surgical Site Infections article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
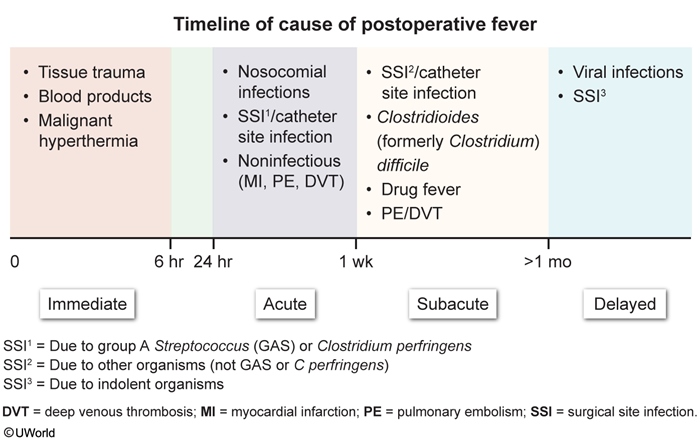
Figure 1
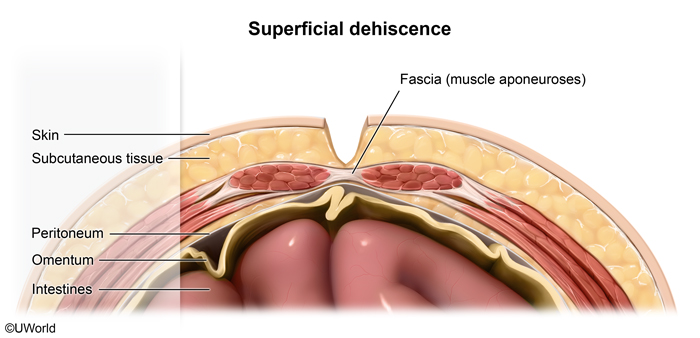
Figure 2
Figure 3
Tables
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3