Malaria
Article Sections
Introduction
Malaria is a protozoal illness caused primarily by 4 species of Plasmodium: P falciparum, P vivax, P ovale, and P malariae. Transmission to humans occurs during blood feeding by an infected female Anopheles mosquito. The pathogen attacks and lyses erythrocytes, leading to febrile paroxysms with constitutional symptoms. Some cases are severe and life-threatening. Malaria is endemic to most tropical and subtropical climates worldwide; >200 million cases are thought to occur annually.
Risk factors
The distribution of malaria worldwide is as follows (Figure 1):
- Sub-Saharan Africa (eg, Nigeria, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda) accounts for >95% of cases worldwide. P falciparum is the leading species.
- In Southeast Asia (eg, India), the Eastern Mediterranean, the Americas, and the Western Pacific, P vivax
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Malaria article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
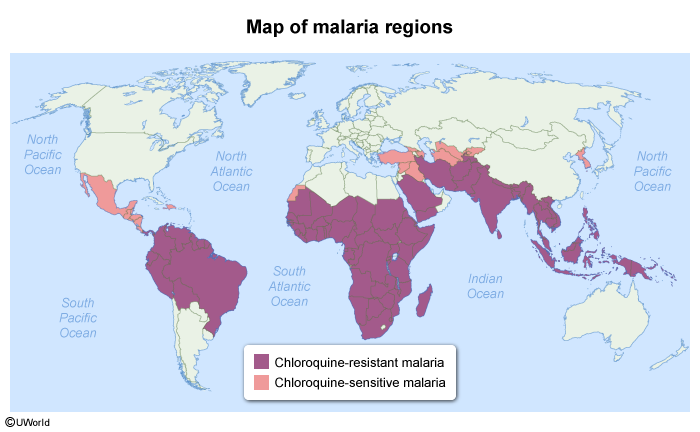
Figure 1
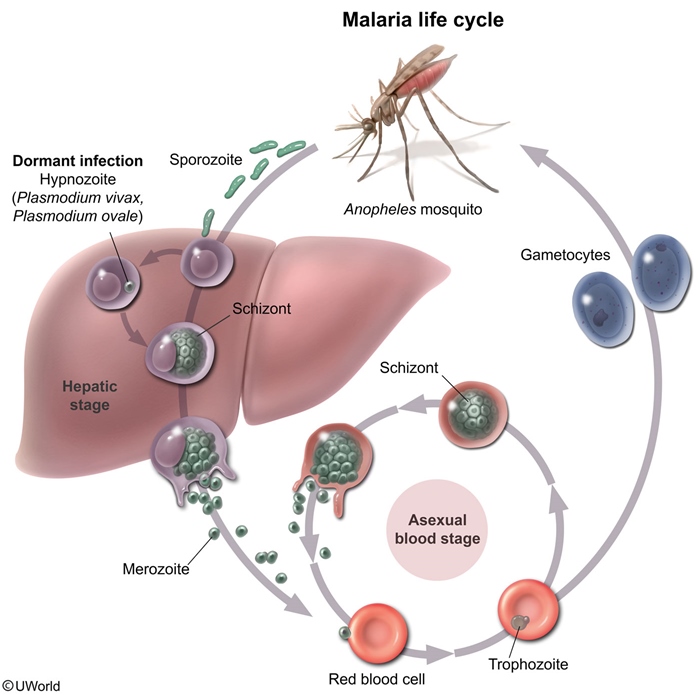
Figure 2
Images
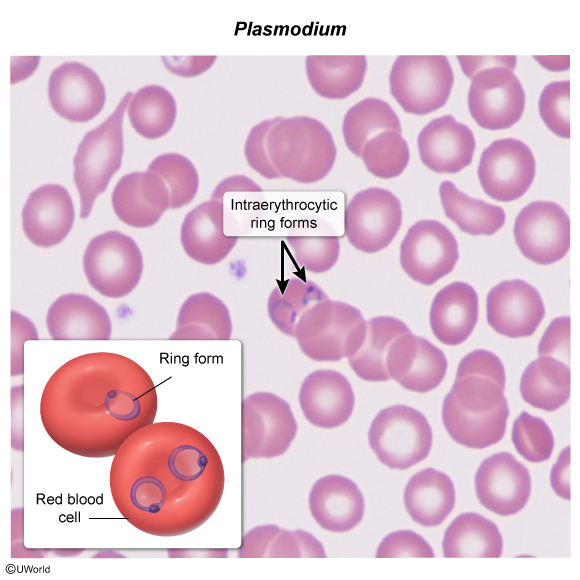
Image 1
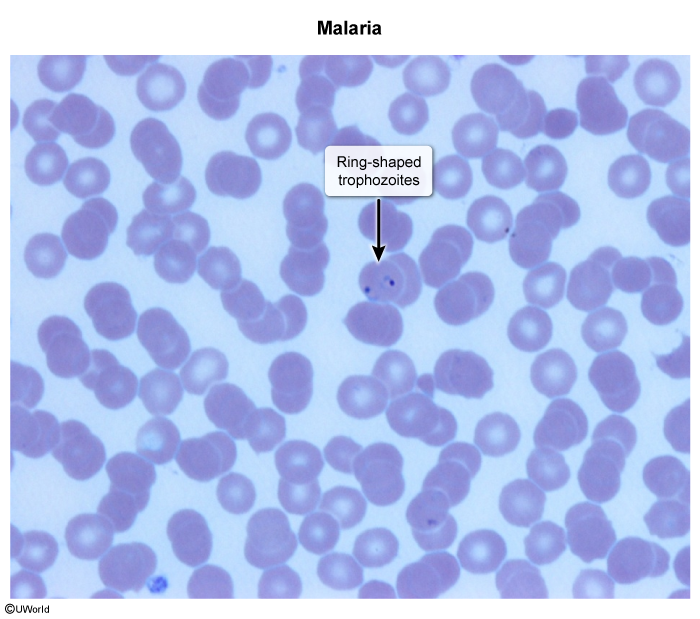
Image 2
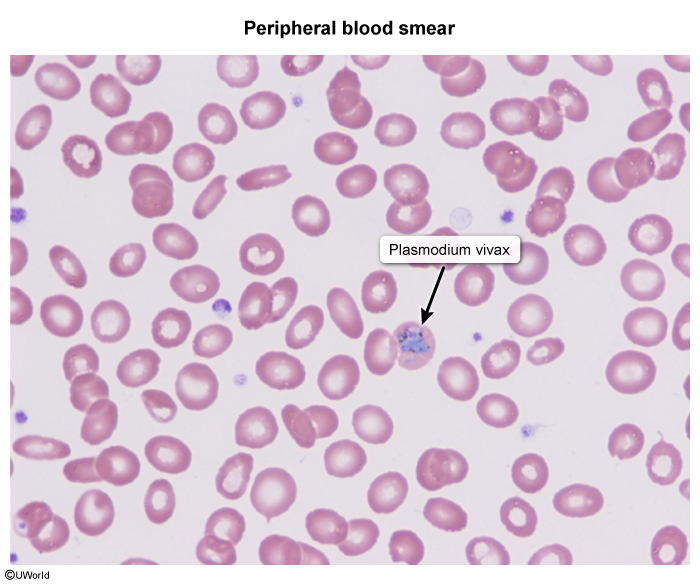
Image 3
Tables
Table 1