Postoperative Fever
Article Sections
Introduction
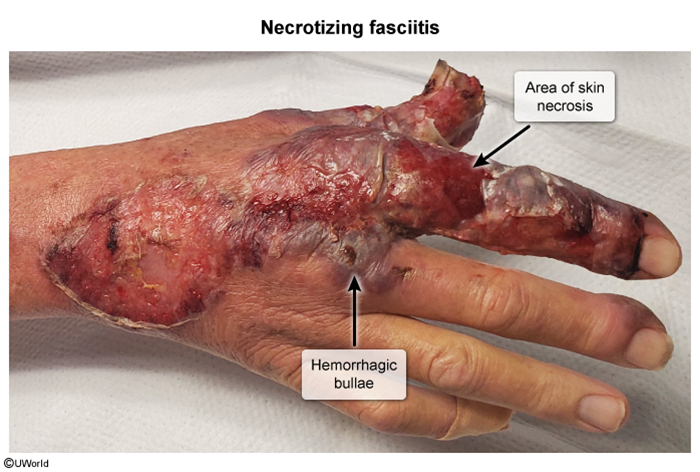
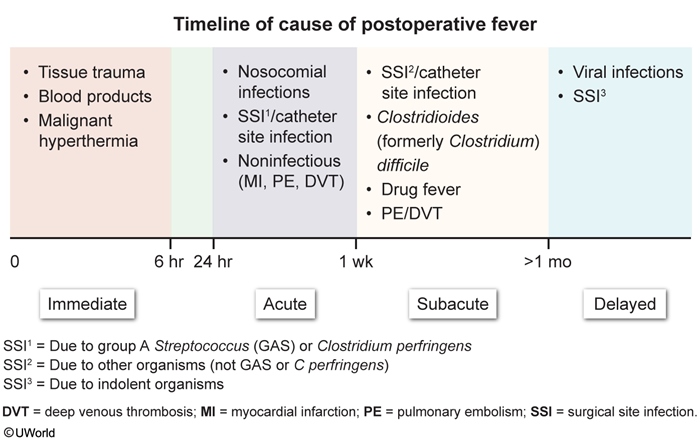
A postoperative fever is defined as a temperature ≥38 °C (100.4°F) following a surgical procedure. Postoperative fevers are common occurrences and arise from many different causes. However, the etiologies generally follow a predictable timeline after surgery (Figure 1), which allows for targeted diagnostic testing. The causes of postoperative fever can be classified with the "5 Ws" mnemonic – wind, wound, water, walk, and wonder drugs (Table 1).
Wind
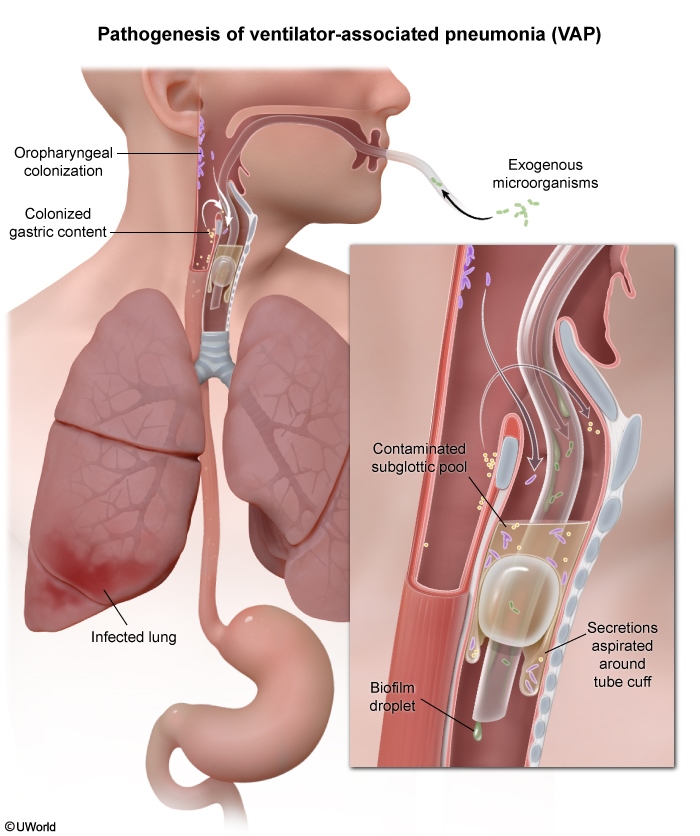
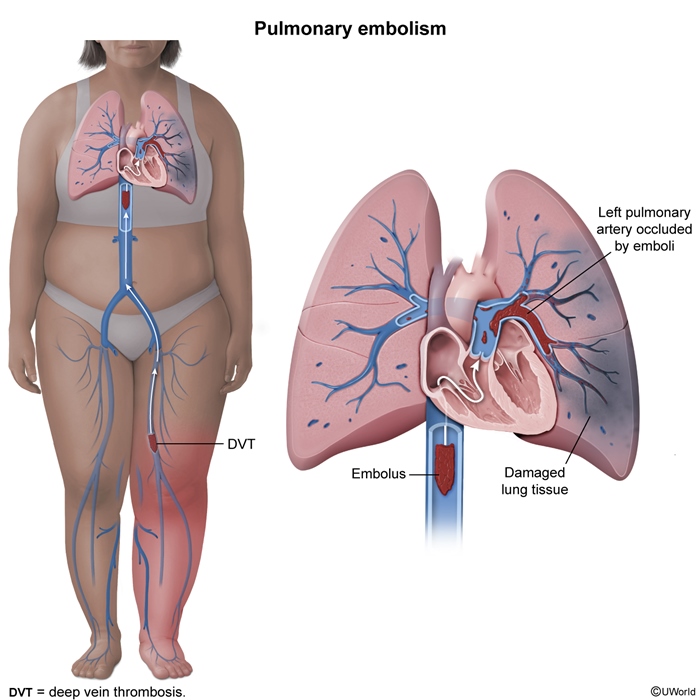
Wind refers to pulmonary causes of fever, which generally occur between 0 and 48 hours postoperatively. Causes include:
Atelectasis is the reversible collapse of lung tissue with poor expansion of alveoli leading to intrapulmonary shunting (ie, perfusion without ventilation). Atelectasis may cause low-grade fever, but it is not an independent cause of fever; therefore, patients should undergo additional evaluation for other potential causes.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Postoperative Fever article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images