Bartonella Henselae Infections
Article Sections
Introduction
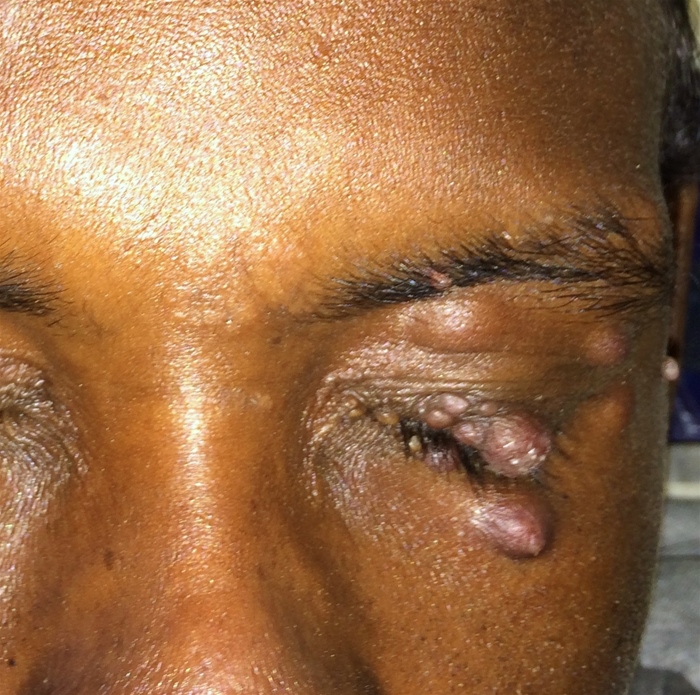
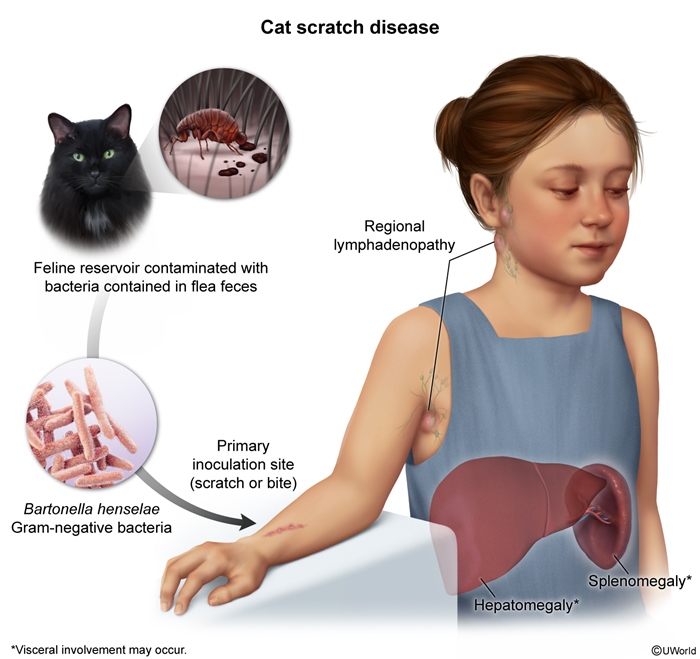
Bartonella henselae is a gram-negative bacterium that is most commonly transmitted by a cat scratch. Cat scratch disease typically presents with chronic, tender, regional lymphadenopathy proximal to the inoculation site; visceral granulomas (eg, on the liver or spleen) can occur. In immunocompromised individuals, B henselae can cause bacillary angiomatosis, a vascular-proliferative disease.
Pathogenesis
Bartonella henselae is a fastidious, gram-negative bacillus or coccobacillus found in cat saliva and is usually transmitted to humans through skin penetration via a cat scratch or bite (Figure 1); it can also be transmitted by direct contact with cat saliva via mucosal surfaces (eg, mouth, eyes) or, rarely, by a bite from an infected flea. Cat-to-cat transmission commonly occurs through fleas; person-to-person transmission does not occur.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Bartonella Henselae Infections article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images