Chlamydia Trachomatis
Article Sections
Introduction
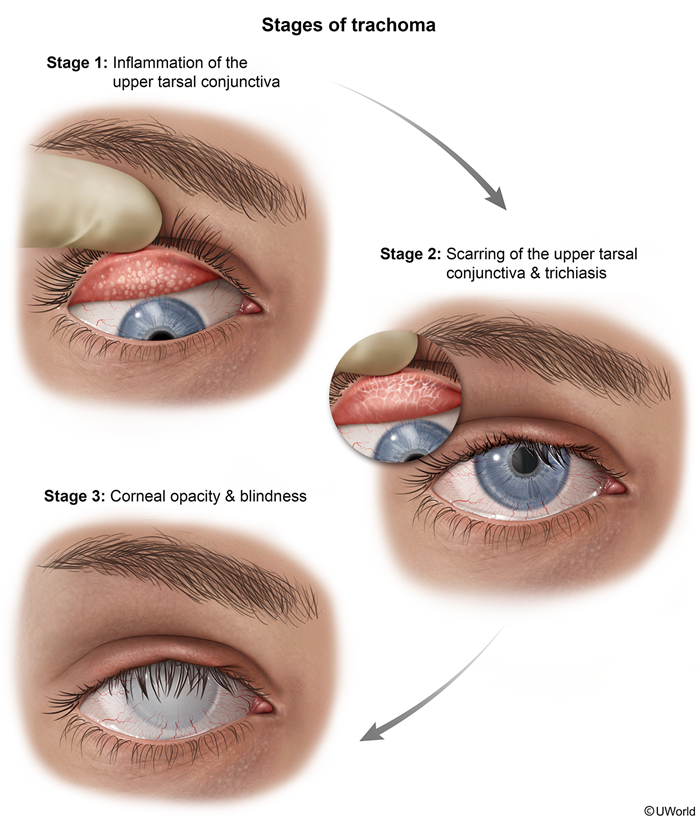
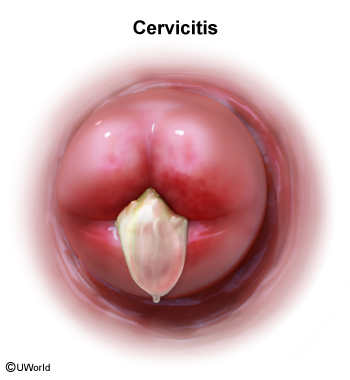
Chlamydia trachomatis, one of the most common bacterial sexually transmitted infections (STIs), is the most common cause of infectious blindness. Infection with this bacterium primarily affects the urogenital tract but can also involve the conjunctivae, respiratory tract, and joints. The infection is often asymptomatic, especially in women, leading to significant underdiagnosis and untreated cases, which can result in serious complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, or ectopic pregnancy.
Pathophysiology
C trachomatis is a gram-negative bacterium with a biphasic life cycle: the extracellular elementary body (EB) and the obligate intracellular reticulate body (RB). It infects epithelial cells and may cause asymptomatic infection or symptomatic disease. The infection process involves the following steps:
- Adherence and entry: The EB is the small, infectious form of
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Chlamydia Trachomatis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures