Pneumonia
Article Sections
Introduction
Pneumonia refers to infection and associated inflammation of the lung parenchyma due to a wide range of commensal and foreign pathogens. In addition to local effects on lung tissue, pneumonia often induces a widespread inflammatory host response. Pneumonia is a major cause of morbidity and mortality, and it is the leading infectious cause of death worldwide.
Classification, microbiology, and pathogenesis
Pneumonia can be classified based on the setting of acquisition (eg, community vs hospital), which correlates closely with the causative microorganism.
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP)- Definition: onset outside hospital settings (eg, at home) or <48 hours after hospital admission
- Microbiology: pathogens, in decreasing order of prevalence, include:
- Typical bacteria (Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis)
- Respiratory viruses (eg, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, SARS-CoV-2)
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Pneumonia article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
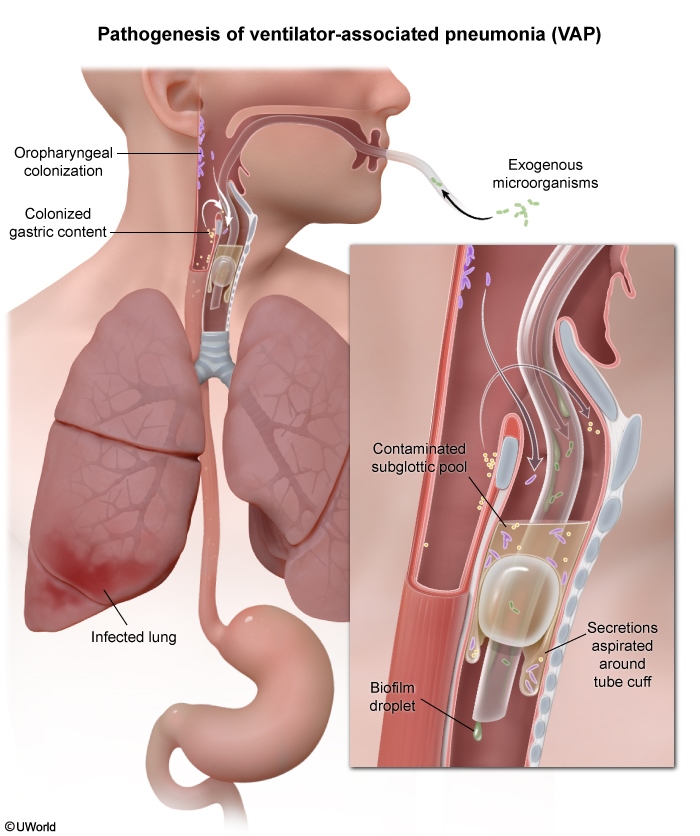
Figure 1
Images
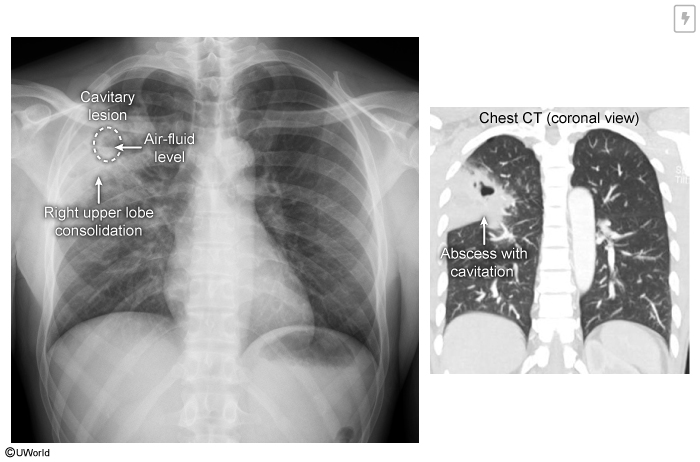
Image 1
Tables
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3
Table 4