Trichomonas Vaginalis
Article Sections
Introduction
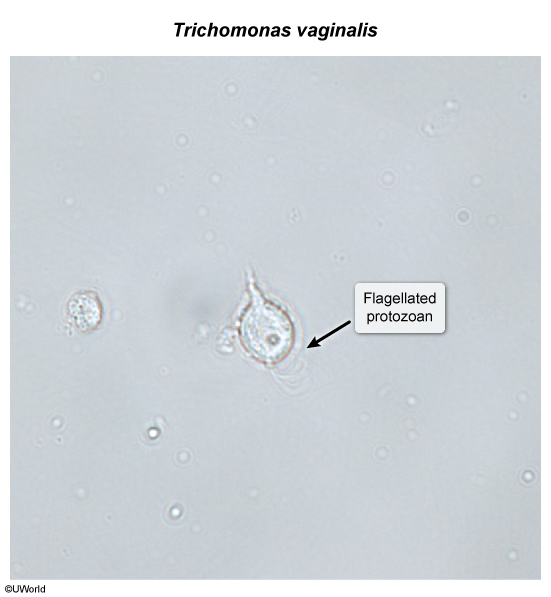
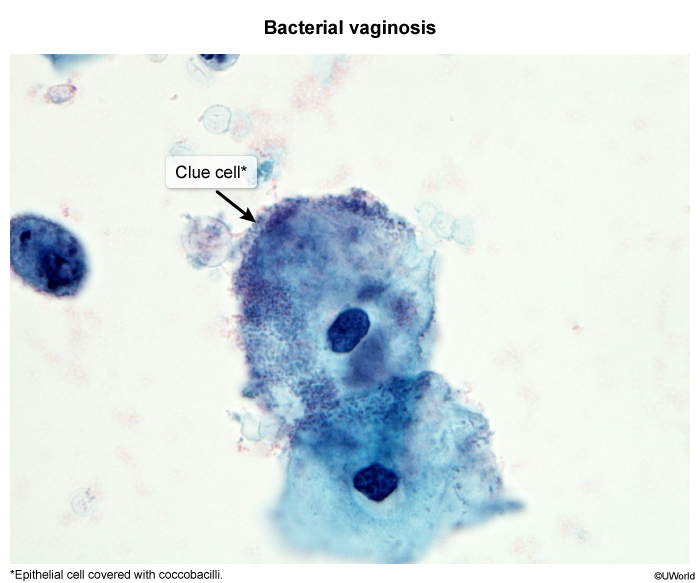
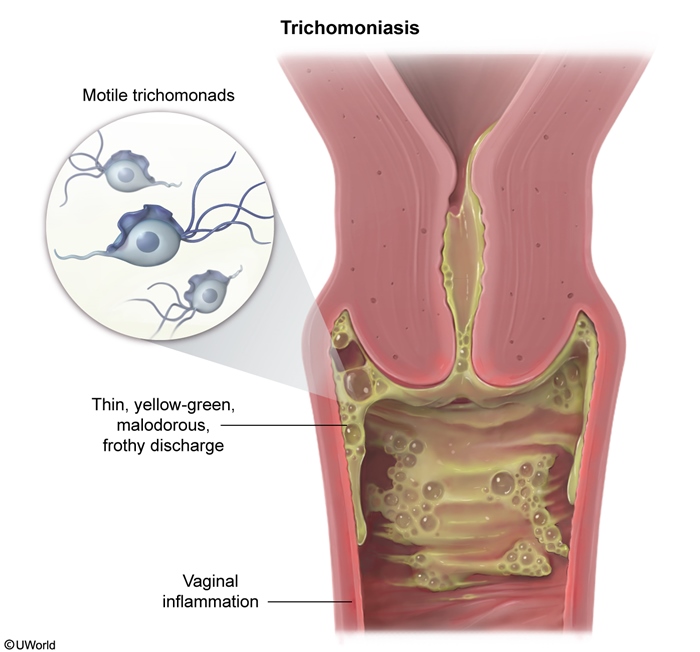
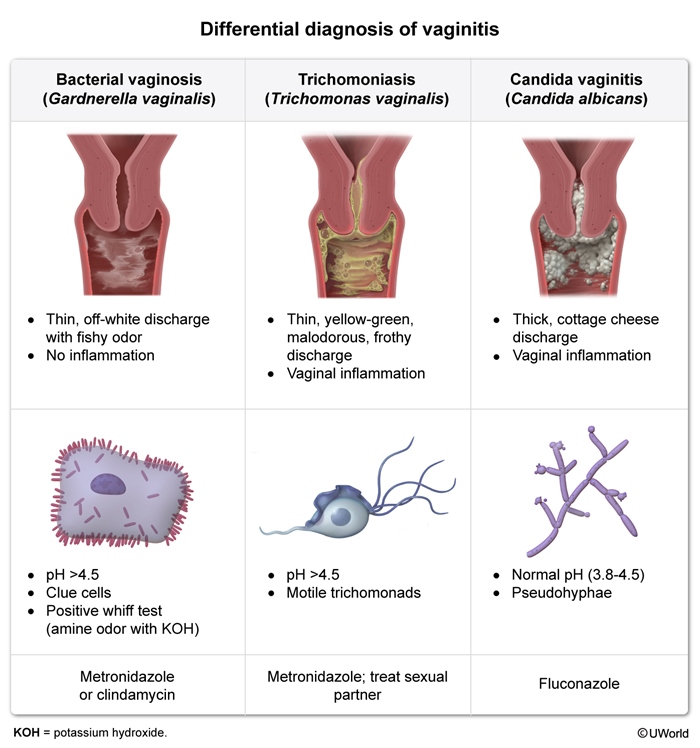
Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects both men and women and is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, a motile, flagellated protozoan. The majority of patients are asymptomatic, but trichomoniasis can cause vaginitis and cervicitis in women and urethritis in men.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
T vaginalis is a sexually transmitted flagellated protozoan that primarily infects the squamous epithelium of the urogenital tract (eg, vagina, urethra, cervix, prostate). The adherence of T vaginalis to the epithelial cells causes direct cytotoxic cell damage and an inflammatory response, contributing to the symptoms of vaginitis in women and urethritis in men.
Risk factors for trichomoniasis include high-risk sexual behaviors (similar to other STIs) and include a history of other STIs, unprotected sexual intercourse, and multiple sexual partners.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Trichomonas Vaginalis article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images