Zika Virus Infection
Article Sections
Introduction
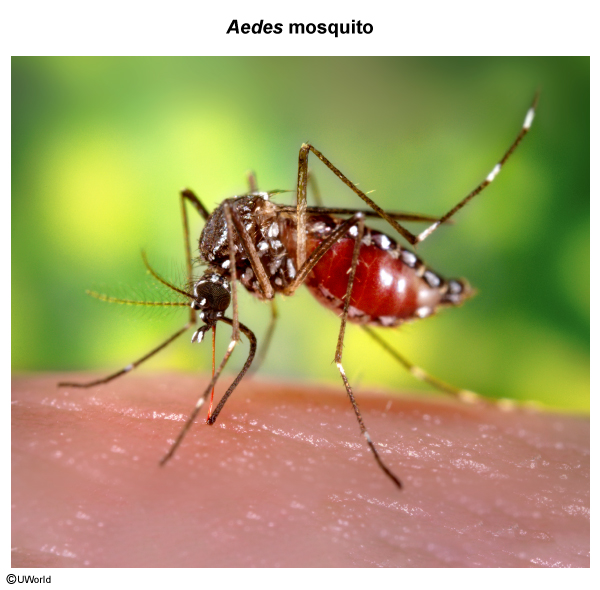
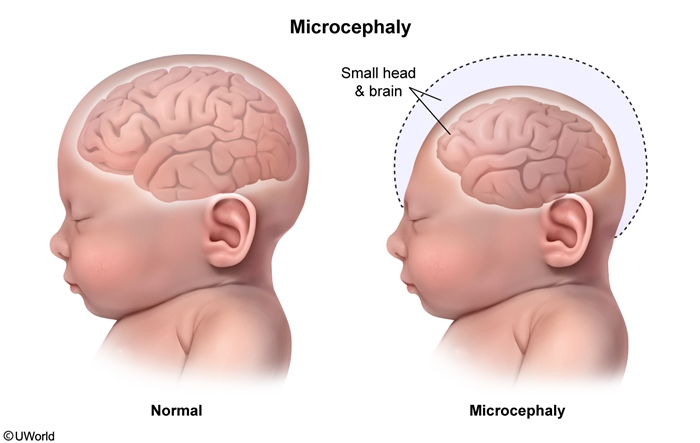
Zika virus (ZIKV) is a flavivirus transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes (Figure 1), with the added potential for human-to-human transmission (eg, maternal-fetal, sexual). Although typically asymptomatic (~80%), ZIKV infection can sometimes cause fever, arthralgia, rash, and conjunctivitis. Several large outbreaks have uncovered ZIKV's association with severe neurologic complications including congenital microcephaly and postnatal Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Epidemiology
The primary mosquito vector of ZIKV is Aedes aegypti, although other Aedes species (eg, Aedes albopictus) have been implicated in outbreaks. ZIKV occurs in the same tropical and subtropical regions inhabited by its mosquito vectors. However, infection can also occur by maternal-fetal transmission (infection crosses the placental barrier), blood product exposure, and sexual contact (from viral shedding in saliva/semen/cervical mucus).
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Zika Virus Infection article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures