Lung Cancer
Article Sections
Introduction
Primary lung cancer (bronchogenic carcinoma) is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Most cases are related to cigarette smoking. Lung cancer is classified into different histologic subtypes (small cell vs non–small cell) that have implications in terms of presentation and management.
Pathogenesis and pathophysiology
Risk factors for primary lung cancer include:
- Cigarette smoking: Firsthand smoking is linked to 85% of cases (~30-fold risk increase compared to never-smokers). Cigarette smoke contains hundreds of carcinogens (aldehydes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nitrosamines) that cause DNA damage through covalent adducts or oxidative radical formation.
- Radon exposure: Radon (222Rn) gas is the second most common cause of lung cancer in the United States. It is a radioactive element found within the Earth (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Lung Cancer article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
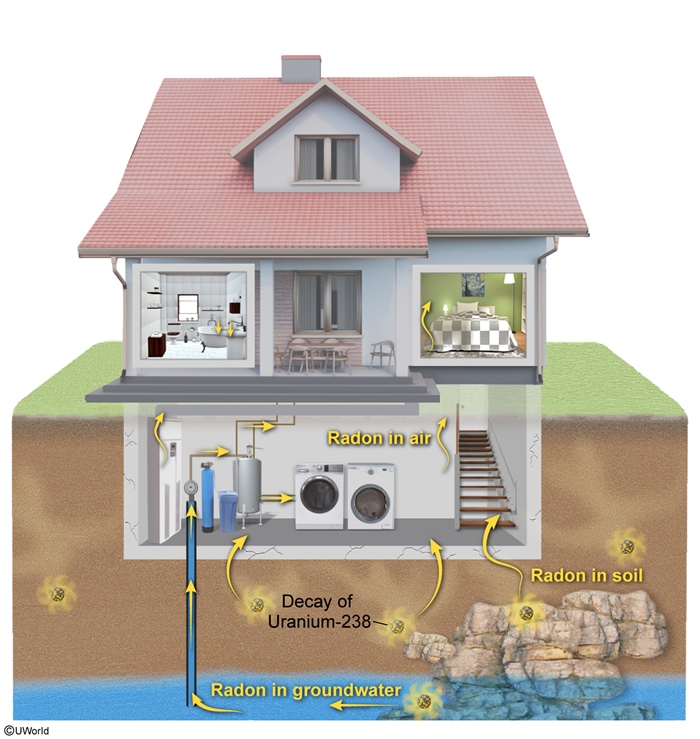
Figure 1
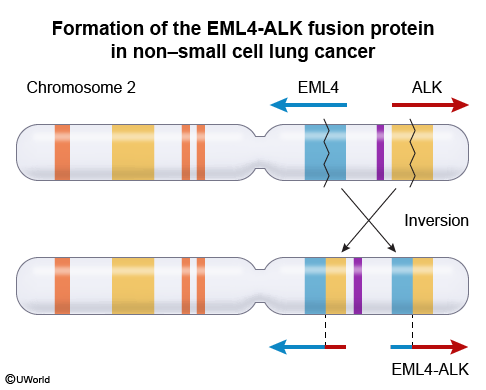
Figure 2
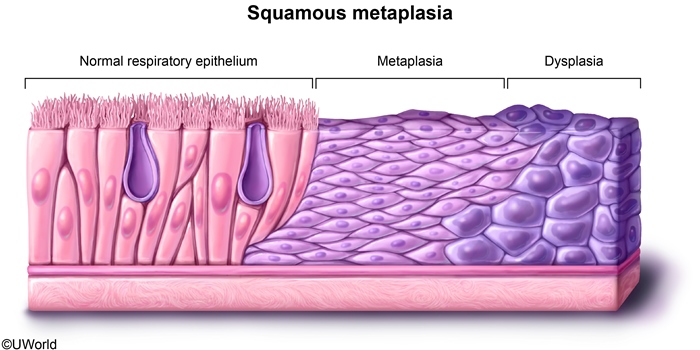
Figure 3
Images
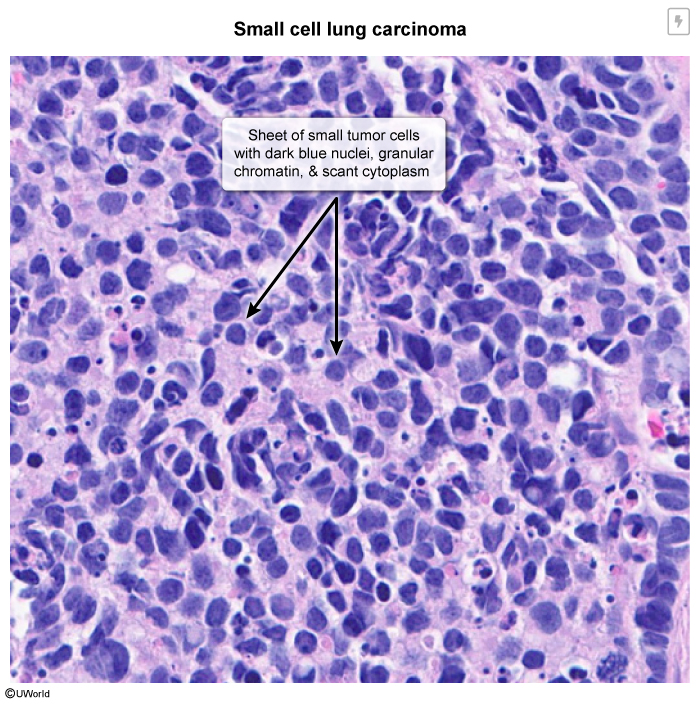
Image 1
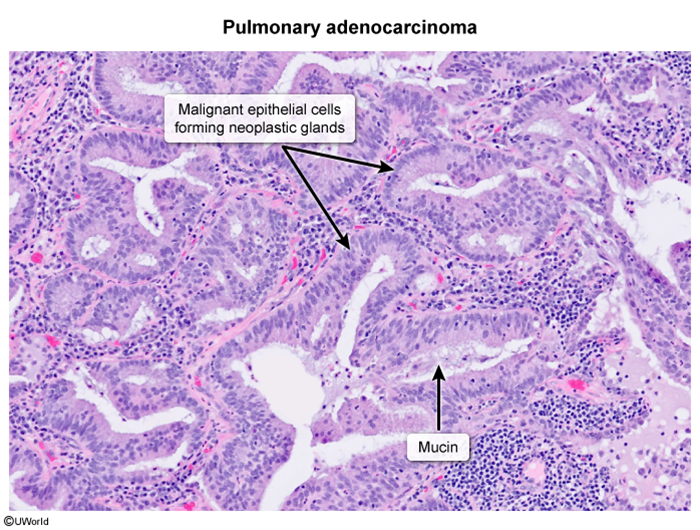
Image 2
Tables
Table 1