Rh Alloimmunization In Pregnancy
Article Sections
Introduction
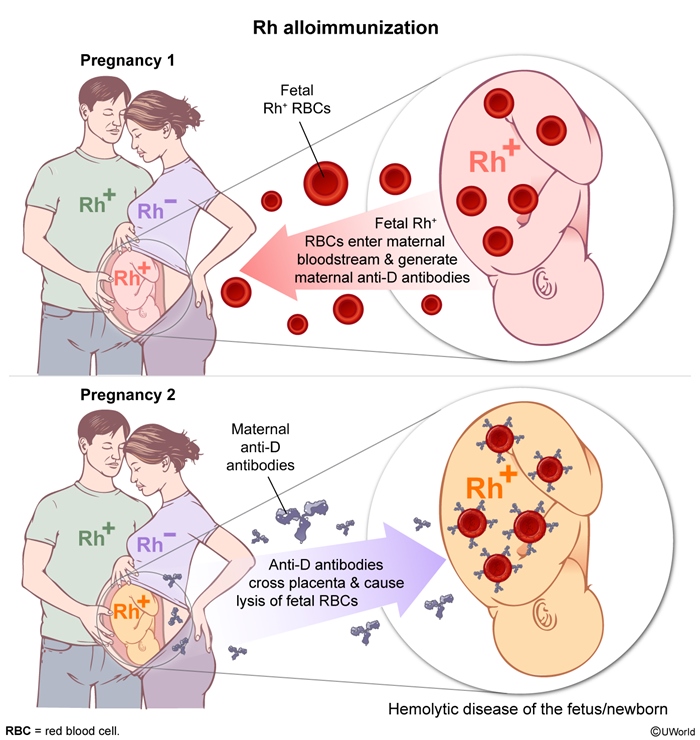
Rh alloimmunization, or Rh incompatibility, is a condition that occurs when an Rh-negative mother develops antibodies against the Rh D antigen on Rh-positive fetal red blood cells (RBCs). This maternal immune response can lead to hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn, which ranges from mild to severe anemia and can result in hydrops fetalis or perinatal death. Preventive strategies with immunoprophylaxis have significantly reduced the incidence of Rh alloimmunization.
Pathogenesis and risk factors
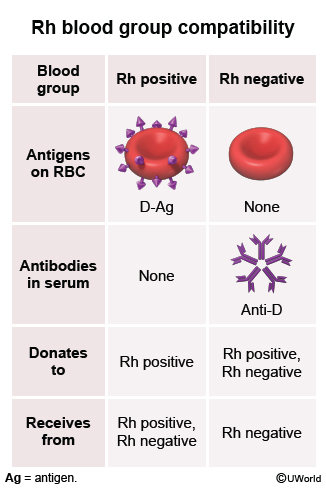
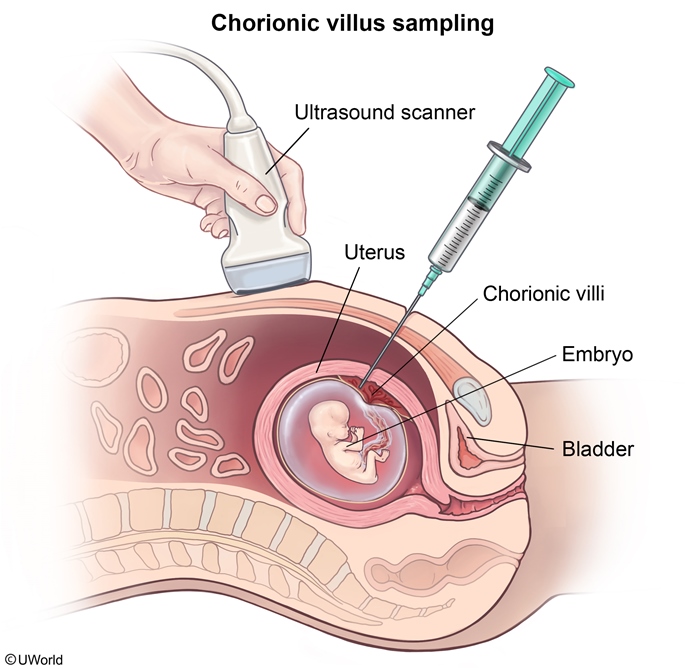
Human RBCs carry a variety of surface proteins depending on an individual's genetic makeup. One of these is the Rh D antigen; individuals who have the Rh D antigen present on RBCs are Rh-positive, and those who lack the antigen are Rh-negative (Figure 1). Rh-negative women have the potential to conceive a fetus who is Rh-positive if the father is Rh-positive.
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Rh Alloimmunization In Pregnancy article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures