Beta Thalassemia
Article Sections
Introduction
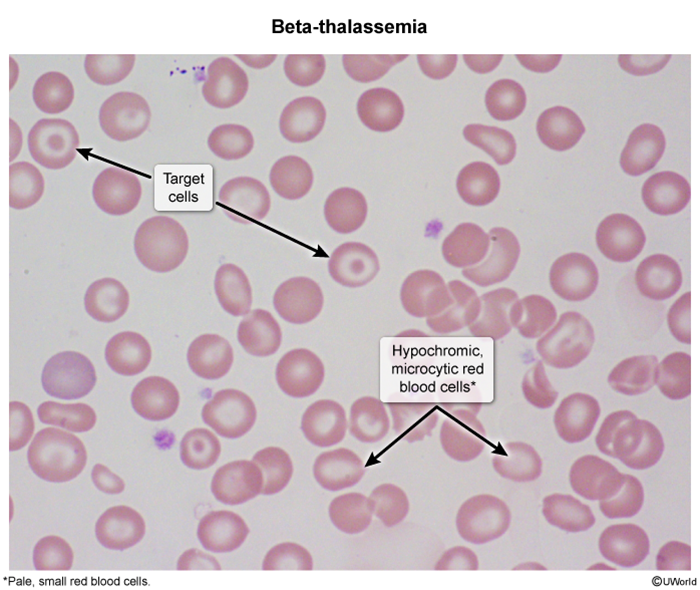
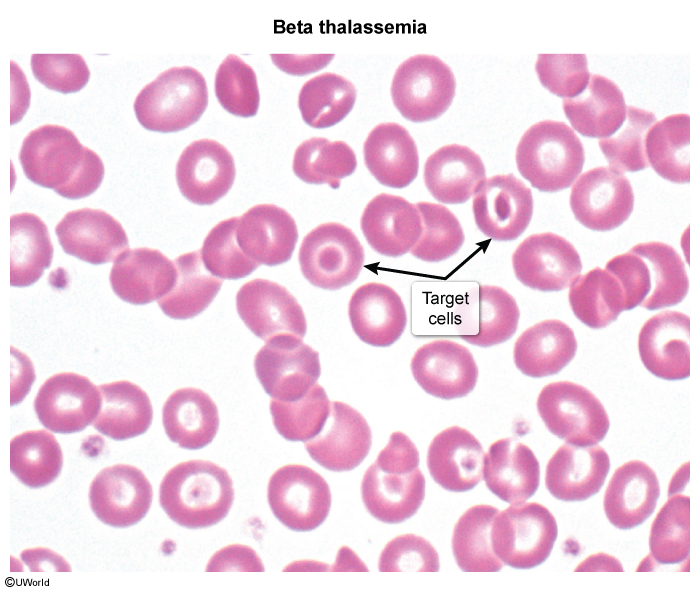
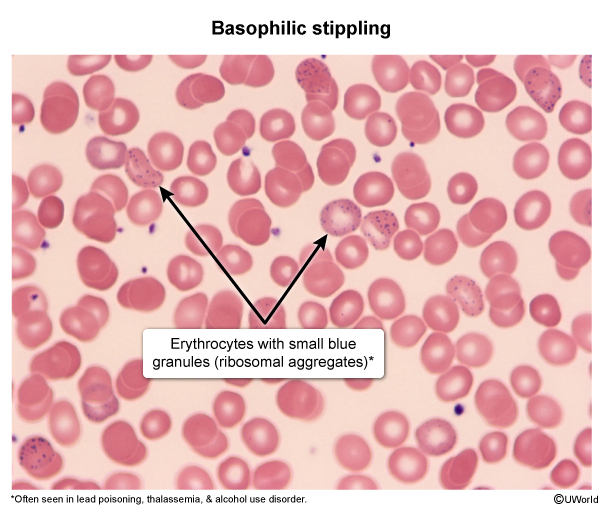
Thalassemias are a group of hereditary anemias characterized by reduced or absent synthesis of one or more globin chains (eg, reduced beta globin chains in beta thalassemia). As a result, hemoglobin production is impaired, and patients can develop microcytic anemia. The clinical presentation varies in severity; in beta thalassemia, this depends on the degree of preserved beta globin chain synthesis.
Pathogenesis
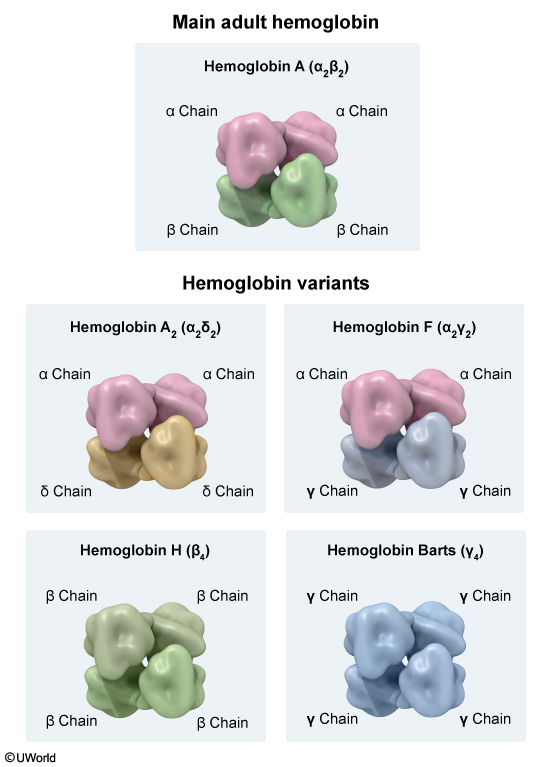
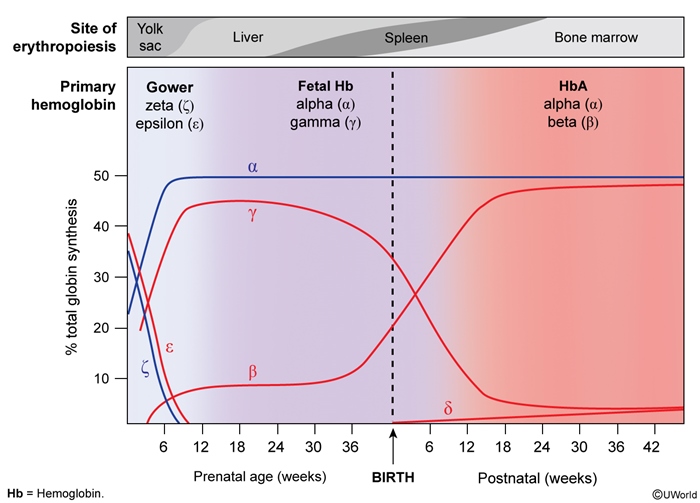
Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells (RBCs). It is composed of 4 subunits, each being a globin chain attached to a heme group containing iron. Normally, 2 different pairs of subunits (eg, a pair of alpha globin chains and a pair of beta globin chains) join to produce hemoglobin (Figure 1). Globin chain synthesis is a highly regulated process that results in a predominant tetramer (ie, hemoglobin type) for each stage of development (eg, embryo, fetus, infant) (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Beta Thalassemia article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images