Alpha Thalassemia
Article Sections
Introduction
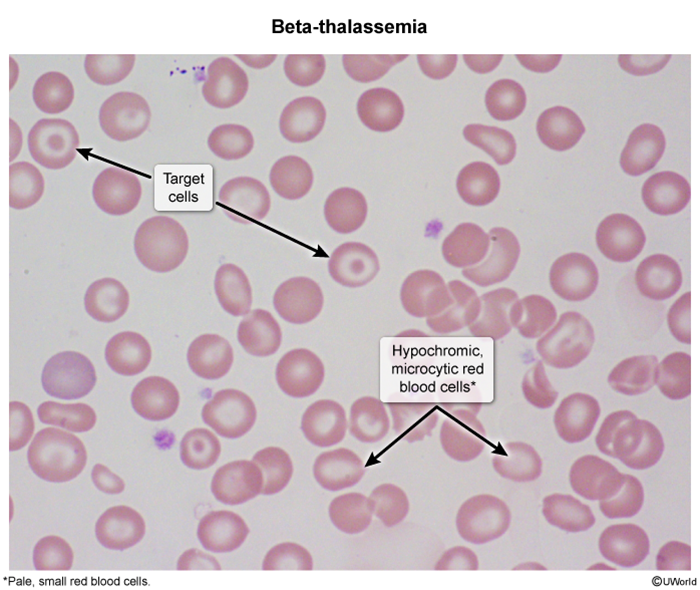
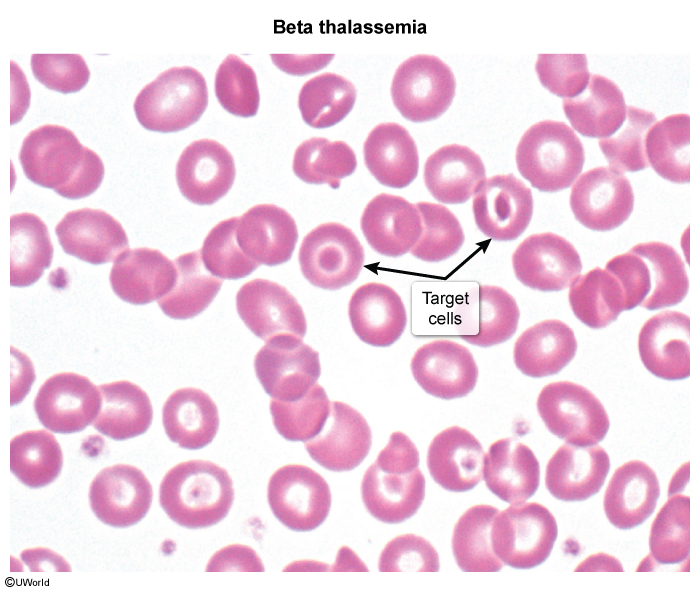
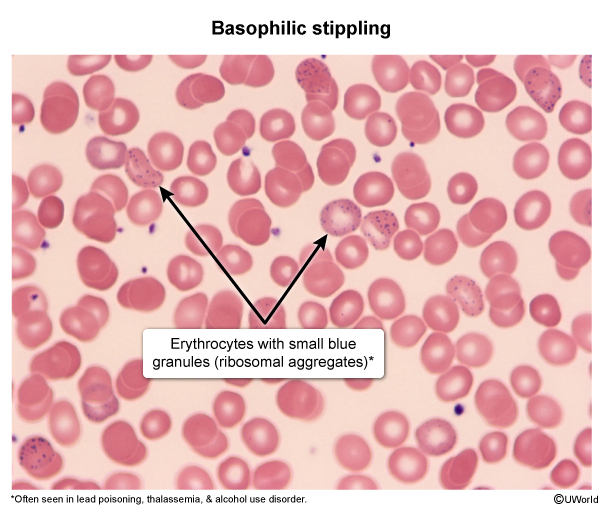
Thalassemias are a group of hereditary anemias characterized by the reduced or absent synthesis of one or more globin chains (eg, reduced alpha globin chain synthesis in alpha thalassemia). As a result, hemoglobin production is impaired, and patients can develop microcytic anemia. The severity of the microcytic anemia and other clinical features of alpha thalassemia varies, depending on the degree of preserved alpha globin chain synthesis.
Pathogenesis
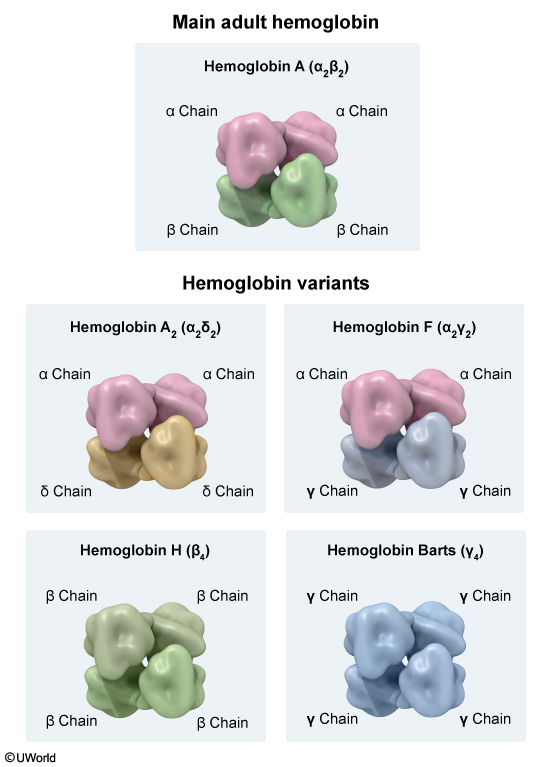
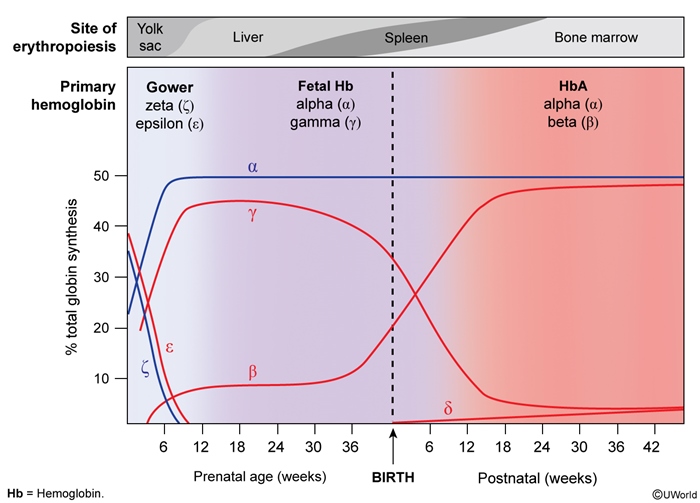
Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in red blood cells (RBCs). It is composed of 4 subunits, each being a globin chain attached to a heme group containing iron. Normally, 2 different pairs of subunits (eg, a pair of alpha globin chains and a pair of beta globin chains) join to produce hemoglobin (Figure 1). Globin chain synthesis is a highly regulated process that results in a predominant tetramer (ie, hemoglobin type) for each stage of development (eg, embryo, fetus, infant) (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Alpha Thalassemia article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images