Von Hippel-Lindau
Article Sections
Introduction
Von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the development of multiple benign and/or malignant tumors throughout the body.
Pathophysiology
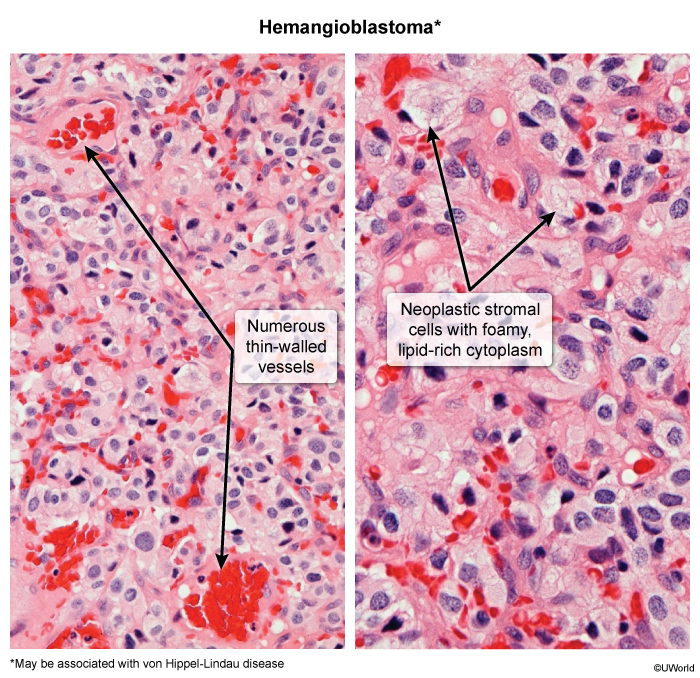
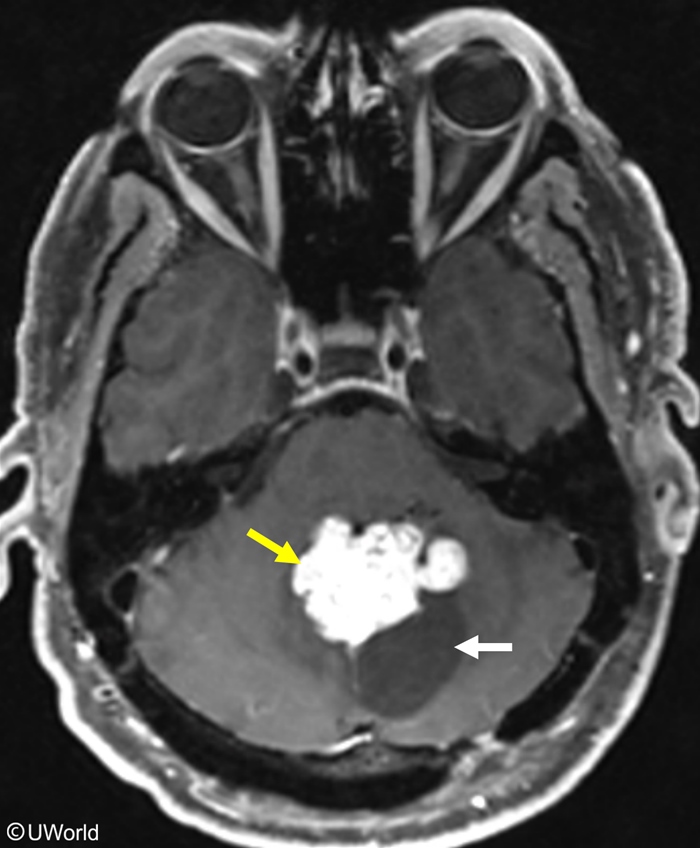
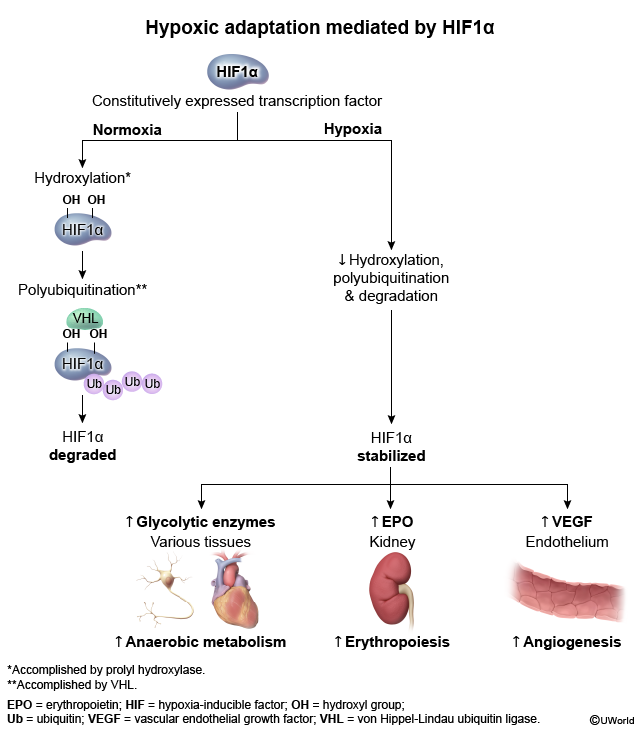
The VHL gene encodes a protein that inhibits the activity of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are involved in oxygen sensing and angiogenesis (Figure 1). VHL mutations lead to constitutive activation of these proteins, resulting in overexpression of multiple angiogenic growth factors (eg, VEG-F, PDG-F) and increased erythropoietin levels that stimulate abnormal growth of blood vessels and the formation of tumors and cysts in various organs.
Genetics
VHL is an autosomal dominant syndrome resulting from germline mutations in the VHL tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3.
Pathology
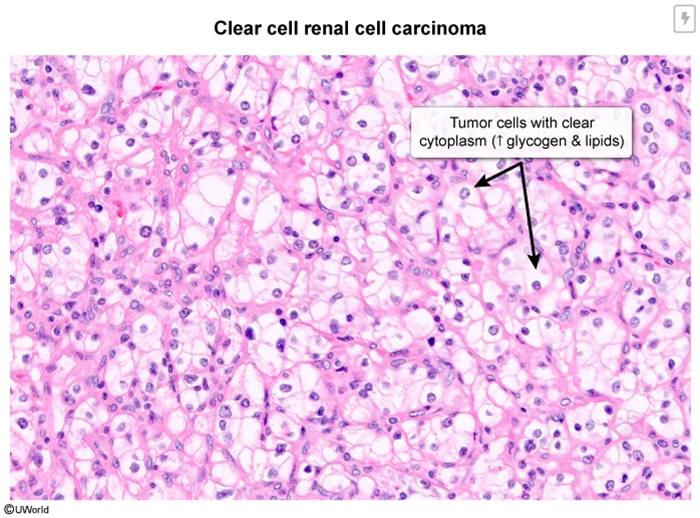
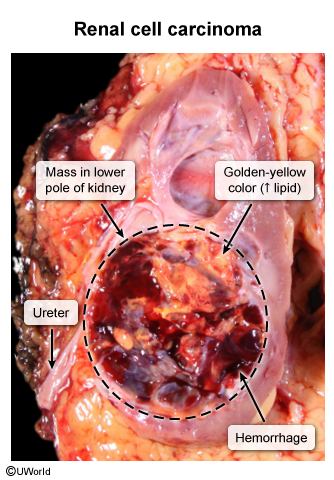
Histopathological examination of VHL-related tumors typically reveals features consistent with their tissue of origin. For example, renal cell carcinomas associated with VHL often exhibit clear cell morphology (
Continue Learning with UWorld
Get the full Von Hippel-Lindau article plus rich visuals, real-world cases, and in-depth insights from medical experts, all available through the UWorld Medical Library.
Unlock Full AccessFigures
Images